25S-Inokosterone
Modify Date: 2025-09-15 20:04:30
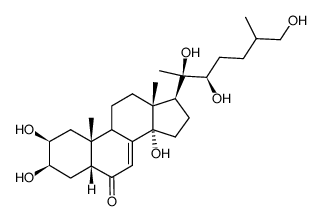
25S-Inokosterone structure
|
Common Name | 25S-Inokosterone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 19595-18-7 | Molecular Weight | 480.63400 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H44O7 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of 25S-Inokosterone25S-Inokosterone is a phytoecdysone in the roots of two same species of A. bidentata Blume and A. japonica Nakai, and two different species of C. capitata Moq and C. officinalis Kuan. 25S-Inokosterone has the potential for the LPS-induced acute kidney injury research[1][2]. |
| Name | inokosterone |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 25S-Inokosterone is a phytoecdysone in the roots of two same species of A. bidentata Blume and A. japonica Nakai, and two different species of C. capitata Moq and C. officinalis Kuan. 25S-Inokosterone has the potential for the LPS-induced acute kidney injury research[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | 25S-Inokosterone (10 μM) significantly promotes the proliferation of LPS-induced NRK52e cells (1.0 μg/mL LPS). 25S-Inokosterone significantly reduces the rate of NRK52e cells apoptosis[1]. 25S-Inokosterone shows weak inhibitory activity for thymus and activation-regulated chemokine expression levels in TNF-α plus IFN-γ induced HaCaT cells. 25S-Inokosterone exhibits the most potent inhibition (80-95% at 200 µg/mL) against TNF-α expression levels in A23187 plus phorbol-myrisrate acetate-induced RBL-2H3 cells[3]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C27H44O7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 480.63400 |
| Exact Mass | 480.30900 |
| PSA | 138.45000 |
| LogP | 1.71150 |
| InChIKey | JQNVCUBPURTQPQ-BMZRUTLMSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(CO)CCC(O)C(C)(O)C1CCC2(O)C3=CC(=O)C4CC(O)C(O)CC4(C)C3CCC12C |
| 25S-Inokosterone |
| Inokosteron |