HMN-154
Modify Date: 2025-09-18 19:15:21
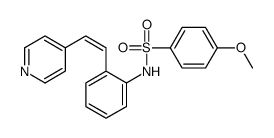
HMN-154 structure
|
Common Name | HMN-154 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 173528-92-2 | Molecular Weight | 366.43400 | |
| Density | 1.313g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 553.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H18N2O3S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 288.6ºC | |
Use of HMN-154HMN-154 is a novel benzenesulfonamide anticancer compound; inhibits KB and colon38 cells with IC50 values of 0.0026 and 0.003 μg/mL, respectively. |
| Name | 4-methoxy-N-[2-(2-pyridin-4-ylethenyl)phenyl]benzenesulfonamide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | HMN-154 is a novel benzenesulfonamide anticancer compound; inhibits KB and colon38 cells with IC50 values of 0.0026 and 0.003 μg/mL, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 0.0026 μg/mL (KB cells), 0.003 μg/mL (colon38 cells)[1] |
| In Vitro | HMN-154 interacts with NF-YB and thereby interrupts the binding of the NF-Y heterotrimer to DNA. NF-YB and thymosin β-10 are specific cellular binding proteins of HMN-154 and that this shared region is necessary for the binding to HMN-154. HMN-154 inhibits DNA binding of NF-Y to the human major histocompatibility complex class II human leukocyte antigen DRA Y-box sequence in a dose-dependent manner. HMN-154 shows very strong cytotoxicity against KB and colon38 cells with an IC50 value of 0.0026 and 0.003 μg/mL, respectively. HMN-154/BSA binds recombinant NF-YB or thymosin β-10 and the binding is inhibited by the addition of HMN-154 as the competitor. The binding between HMN-154 and NF-YB is specific and depends on its cytotoxicity[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Cells are seeded into a 96-well microplate at a cell density of 10000/well. Drug is added on the next day, and the plate then is incubated for 72 h at 37°C. The growth inhibitory concentration is measured by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide assay[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.313g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 553.7ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H18N2O3S |
| Molecular Weight | 366.43400 |
| Flash Point | 288.6ºC |
| Exact Mass | 366.10400 |
| PSA | 76.67000 |
| LogP | 5.21520 |
| Vapour Pressure | 2.67E-12mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.651 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
|
~% 
HMN-154 CAS#:173528-92-2 |
| Literature: Nippon Shinyaku Company, Limited Patent: US5972976 A1, 1999 ; |
| HMN-154 |
![2-[(E)-2-(4-pyridinyl)ethenyl]aniline structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/234/138386-71-7.png)