Isatidine
Modify Date: 2025-09-16 19:24:01
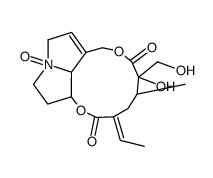
Isatidine structure
|
Common Name | Isatidine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 15503-86-3 | Molecular Weight | 367.39400 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H25NO7 | Melting Point | 138ºC (Decomp) | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of IsatidineRetrorsine N-oxide, an N-oxide of pyrrolizidine alkaloid, is a carcinogen. Retrorsine N-oxide-derived DNA adducts are common toxicological biomarkers of pyrrolizidine alkaloid N-oxides[1][2]. |
| Name | isatidine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Retrorsine N-oxide, an N-oxide of pyrrolizidine alkaloid, is a carcinogen. Retrorsine N-oxide-derived DNA adducts are common toxicological biomarkers of pyrrolizidine alkaloid N-oxides[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | Retrorsine N-oxide produces DNA adducts, the common biological biomarker of PA-induced liver tumor formation[1]. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 138ºC (Decomp) |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H25NO7 |
| Molecular Weight | 367.39400 |
| Exact Mass | 367.16300 |
| PSA | 122.49000 |
| LogP | 0.13660 |
| RIDADR | UN 1544 |
|---|---|
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
| Retrorsine N-oxide |
| (3Z,5R,6S,14aR,14bR)-3-ethylidene-6-hydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-5-methyl-3,4,5,6,9,11,13,14,14a,14b-decahydro[1,6]dioxacyclododecino[2,3,4-gh]pyrrolizine-2,7-dione 12-oxide |