Celgosivir (hydrochloride)
Modify Date: 2025-08-26 09:06:25
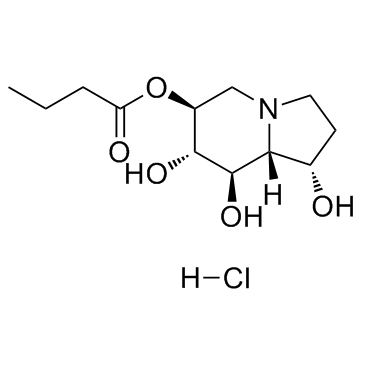
Celgosivir (hydrochloride) structure
|
Common Name | Celgosivir (hydrochloride) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 141117-12-6 | Molecular Weight | 295.76000 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 422.9ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H22ClNO5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 209.6ºC | |
Use of Celgosivir (hydrochloride)Celgosivir hydrochloride (MDL 28574A) is an α-glucosidase I inhibitor; inhibits bovine viral diarrhoea virus (BVDV) with an IC50 of 1.27 μM in in vitro assay. |
| Name | [(1S,6S,7S,8R,8aR)-1,7,8-trihydroxy-1,2,3,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydroindolizin-6-yl] butanoate,hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Celgosivir hydrochloride (MDL 28574A) is an α-glucosidase I inhibitor; inhibits bovine viral diarrhoea virus (BVDV) with an IC50 of 1.27 μM in in vitro assay. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 1.27 μM (α-glucosidase I)[1] |
| In Vitro | Celgosivir is more effective (IC50=20 μM) than the parent molecule (IC50=254 ,uM) at causing the accumulation of glucosylated oligosaccharides in HIV-infected cells by inhibition of glycoprotein processing. Celgosivir exhibits potent antiviral activity against HIV-1 with an IC50 of 2.0±2.3 μM[1]. Bovine viral diarrhoea virus (BVDV) is a closely related virus of hepatitis C virus (HCV). Celgosivir inhibits BVDV with IC50 values of 16 and 47 μM in plaque assay and cytopathic effect assay, respectively[2]. Celgosivir inhibits DENV2 replication with an EC50 of 0.2 μM. The EC50 values against DENV1, 3 and 4 are less than 0.7 μM[3]. |
| In Vivo | Celgosivir fully protects AG129 mice from lethal infection with a mouse adapted dengue virus at a dose of 50 mg/kg twice daily (BID) for 5 days and is effective even after 48 h delayed treatment. The protection by celgosivir is dose- and schedule-dependent and that a twice-a-day regimen of 50, 25 or 10 mg/kg is more protective than a single daily dose of 100 mg/kg. Pharmacokinetics studies of celgosivir in mice shows that it rapidly metabolizes to castanospermine[4]. During primary infection with a mouse-adapted DENV strain S221, mice shows increased viremia on day 3, yet 80% survived day 10 with virus completely cleared by day 8[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | The enzymatic assays are performed at 37°C for 60 min in a total volume of 80 μL which contains 10,000 cpm of [3H]G3M7_9N substrate, 100 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 6.8), and purified a-glucosidase I, and the mixture is chromatographed on a ConA sepharose column. The liberated monosaccharides, which are obtained in the first two fractions, are plotted as radioactivity released against compound concentration to determine an IC50 for enzyme inhibition[1]. |
| Cell Assay | The cytotoxicity of Celgosivir is measured by the Cell titer-Glo Luminescent cell viability assay. The luminescence signals for cells treated with the test compounds are compared to those for cells treated with the maximum tolerated DMSO to determine the 50% cytotoxic concentration[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: To model ADE, mice are injected i.p. with 20 μg /mouse of mouse monoclonal antibody against DENV E protein one day prior to infection. For treatment during infection, celgosivir (50 mg/kg) is injected i.p. twice daily for 5 days, starting from day 0, 1 or 2. Blood is collected at days 1, 3 and 7 by submandibular bleeding. Survival of mice is followed until day 10 and survival curves are plotted[3]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 422.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H22ClNO5 |
| Molecular Weight | 295.76000 |
| Flash Point | 209.6ºC |
| Exact Mass | 295.11900 |
| PSA | 90.23000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 6.34E-09mmHg at 25°C |
| InChIKey | KXNZMBFOWDNCRU-QVMZSJACSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCC(=O)OC1CN2CCC(O)C2C(O)C1O.Cl |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
|
~77% 
Celgosivir (hyd... CAS#:141117-12-6 |
| Literature: Aventis Pharmaceuticals Inc. Patent: EP983270 B1, 2004 ; Location in patent: Page 8 ; |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| Celgosivir hydrochloride (USAN) |
| Celgosivir HCl |
| UNII-70U2NQU0FP |
| Celgosivir hydrochloride |
| 6-O-Butyryltanosopermine HCl |
| 6-O-butyryltanospermine hydrochloride |
| Celgosivir (hydrochloride) |