(D-Lys(nicotinoyl)1,β-(3-pyridyl)-Ala3,3,4-dichloro-D-Phe5,Asn6,D-Trp7·9,Nle11)-Substance P trifluoroacetate salt
Modify Date: 2025-09-27 10:46:00
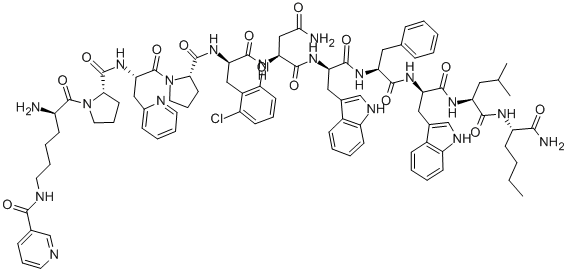
(D-Lys(nicotinoyl)1,β-(3-pyridyl)-Ala3,3,4-dichloro-D-Phe5,Asn6,D-Trp7·9,Nle11)-Substance P trifluoroacetate salt structure
|
Common Name | (D-Lys(nicotinoyl)1,β-(3-pyridyl)-Ala3,3,4-dichloro-D-Phe5,Asn6,D-Trp7·9,Nle11)-Substance P trifluoroacetate salt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 129176-97-2 | Molecular Weight | 1668.79 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C86H104Cl2N18O13 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of (D-Lys(nicotinoyl)1,β-(3-pyridyl)-Ala3,3,4-dichloro-D-Phe5,Asn6,D-Trp7·9,Nle11)-Substance P trifluoroacetate saltSpantide II, an undecapeptide substance P (SP) analog, is a potent neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) antagonist. Spantide II binds with NK-1R and blocks proinflammatory activities associated with SP. Spantide II can be used in the research of inflammatory skin disorders, such as psoriasis and contact dermatitis[1][2][3]. |
| Name | spantide II |
|---|
| Description | Spantide II, an undecapeptide substance P (SP) analog, is a potent neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) antagonist. Spantide II binds with NK-1R and blocks proinflammatory activities associated with SP. Spantide II can be used in the research of inflammatory skin disorders, such as psoriasis and contact dermatitis[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
NK1 |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C86H104Cl2N18O13 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 1668.79 |
| InChIKey | AZZJAARMZMEIHY-BBKUSFMUSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCC(NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(Cc1c[nH]c2ccccc12)NC(=O)C(Cc1ccccc1)NC(=O)C(Cc1c[nH]c2ccccc12)NC(=O)C(CC(N)=O)NC(=O)C(N)Cc1ccc(Cl)c(Cl)c1)C(=O)N(C(=O)C1CCCN1C(=O)C(N)CCCCNC(=O)c1cccnc1)C(=O)C1CCCN1C(=O)C(N)Cc1cccnc1 |