Protosappanin A
Modify Date: 2025-08-22 22:11:35
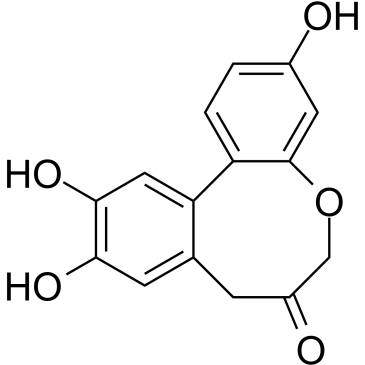
Protosappanin A structure
|
Common Name | Protosappanin A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 102036-28-2 | Molecular Weight | 272.25 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 613.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H12O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 238.8±25.0 °C | |
Use of Protosappanin AProtosappanin A (PTA), an immunosuppressive ingredient and major biphenyl compound isolated from Caesalpinia sappan L, suppresses JAK2/STAT3-dependent inflammation pathway through down-regulating the phosphorylation of JAK2 and STAT3[1]. |
| Name | Protosappanin A |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Protosappanin A (PTA), an immunosuppressive ingredient and major biphenyl compound isolated from Caesalpinia sappan L, suppresses JAK2/STAT3-dependent inflammation pathway through down-regulating the phosphorylation of JAK2 and STAT3[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
JAK2 STAT3 |
| In Vitro | Protosappanin A (PTA: 12.5, 25, 50 μM, 24 hours) significantly inhibits the production of TNF-α and IL-1β in LPS-activated BV2 microglia. And the mRNA expressions of IL-6, IL-1β, and MCP-1 are reduced by PTA in a dose-dependent manner in BV2 microglial cell line[1]. Protosappanin A (PTA: 12.5, 25, 50 μM, 24 hours) suppresses JAK2/STAT3-dependent inflammation pathway through down-regulating the phosphorylation of JAK2 and STAT3, as well as STAT3 nuclear translocation against LPS treatment[1]. Protosappanin A (PTA: 12.5, 25, 50 μM, 24 hours) shows obvious effect on disturbing the interaction of transmembrane protein CD14 with Toll-like receptor-4, resulting in the inhibition of NF-κB-dependent oxidative and nitrative stress in LPS-induced BV2 microglia[2]. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: Murine BV2 microglial cell line. Concentration: 12.5, 25, 50 μM. Incubation Time: 24 hours. Result: Inhibits the releases of NO, TNF-α and IL-1β in LPS-induced BV2 cells. Attenuated IL-6, IL-1β and MCP-1 gene expressions in the LPS-induced BV2 cells. Suppressed JAK2/STAT3 pathway activation in the LPS-induced BV2 cells. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 613.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C15H12O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 272.25 |
| Flash Point | 238.8±25.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 272.068481 |
| PSA | 86.99000 |
| LogP | 1.20 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.689 |
| InChIKey | MUKYVRVYBBYJSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C1COc2cc(O)ccc2-c2cc(O)c(O)cc2C1 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |
| 6H-Dibenz(b,d)oxocin-7(8H)-one,3,10,11-trihydroxy |
| 3,10,11-Trihydroxy-6H-dibenzo[b,d]oxocin-7(8H)-one |
| Sappanol B |
| 6H-Dibenz(b,d)oxocin-7(8H)-one, 3,10,11-trihydroxy- |
| 6H-Dibenz[b,d]oxocin-7(8H)-one, 3,10,11-trihydroxy- |
![[1,1'-Biphenyl]-2,2',4,4'-tetrol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/432/4371-31-7.png) CAS#:4371-31-7
CAS#:4371-31-7 CAS#:120-80-9
CAS#:120-80-9 CAS#:108-46-3
CAS#:108-46-3