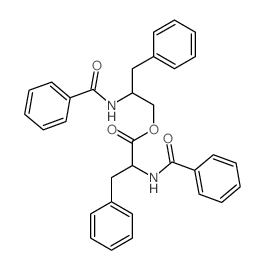
63631-36-7
| Name | asperphenamate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Auranamide
N-benzoylphenylalaninyl-N-benzoylphenylalaninate N-Benzoyl-L-phenylalanine (S)-2-benzoylamino-3-phenylpropyl ester (2S)-2-(Benzoylamino)-3-phenylpropanoic acid (2S)-2-(benzoylamino)-3-phenylpropyl ester |
| Description | Asperphenamate, a fungal metabolite of Aspergillus flatiipes with anti-cancer effect, exhibits IC50 values of 92.3 μM, 96.5 μM and 97.9 μM in T47D, MDA-MB-231 and HL-60 cells, respectively[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Asperphenamate can inhibit cancer cell proliferation by fully inducing autophagy. asperphenamate showed inhibition effects against cathepsin L. At the same time, it also displayed weak inhibitory ability against cathepsin S. |
| References |
[1]. Alice M.Clark, et al. Synthesis of asperphenamate, a novel fungal metabolite. Phytochemistry |
| Density | 1.198g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 774.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C32H30N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 506.59200 |
| Flash Point | 422.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 506.22100 |
| PSA | 84.50000 |
| LogP | 5.39400 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.611 |