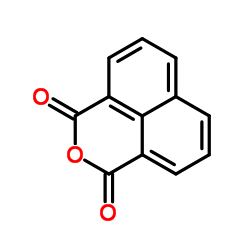
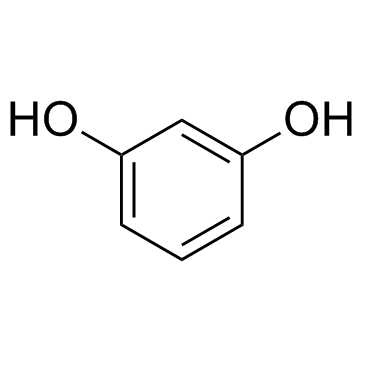
41307-63-5
| Name | Resorcinolnaphthalein |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
3',6'-Dihydroxy-3H-spiro[benzo[de]isochromene-1,9'-xanthen]-3-one
Resorcinolnaphthalin resorcinalnaphthalein 3',6'-Dihydroxy-spiro[benz[de]isochromen-1,9'-xanthen]-3-on 3',6'-dihydroxyspiro[1H,3H-naphtho[1,8-cd]pyran-1,9'-[9H]xanthen]-3-one 3',6'-dihydroxy-spiro[benz[de]isochromene-1,9'-xanthen]-3-one |
| Description | Resorcinolnaphthalein is a specific angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) enhancer and activates ACE2 activity with an EC50 value of 19.5 μM. Resorcinolnaphthalein can be used for the investigation of hypertension and renal fibrosis[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
EC50: 19.5 μM (ACE2)[1] |
| In Vitro | Resorcinolnaphthalein (100 μM) and XNT enhances ACE2 activity in a dose-dependent manner with EC50 values of 19.5 μM and 20.1 μM, respectively[1]. ACE2 is an effective enzyme in attenuating fibrosis and structural remodeling. Enhancement of ACE2 activity has beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system and protects against hypertension induced pathophysiology[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 688.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C24H14O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 382.365 |
| Flash Point | 249.7±25.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 382.084137 |
| PSA | 75.99000 |
| LogP | 4.21 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.830 |
|
~% 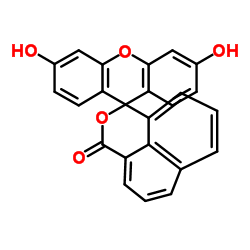
41307-63-5 |
| Literature: Terrisse Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, 1885 , vol. 227, p. 139 |
|
~% 
41307-63-5 |
| Literature: Mason Journal of the Chemical Society, 1924 , vol. 125, p. 2117 |