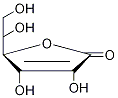
1331939-77-5
| Name | L-Ascorbic Acid-13C6 |
|---|
| Description | L-Ascorbic acid-13C6-1 (L-Ascorbate-1; Vitamin C-13C6-1) is a 13C labeled L-Ascorbic acid (HY-B0166)[1]. L-Ascorbic acid (L-Ascorbate), an electron donor, is an endogenous antioxidant agent. L-Ascorbic acid inhibits selectively Cav3.2 channels with an IC50 of 6.5 μM. L-Ascorbic acid is also a collagen deposition enhancer and an elastogenesis inhibitor[2][3][4]. L-Ascorbic acid exhibits anti-cancer effects through the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and selective damage to cancer cells[5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Melting Point | 187-189°C |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | 13C6H8O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 182.08 |
| Appearance | Solid | White to Pale Beige |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer, Under Inert Atmosphere |
| Water Solubility | DMSO (Sparingly), Methanol (Slightly, Sonicated) |