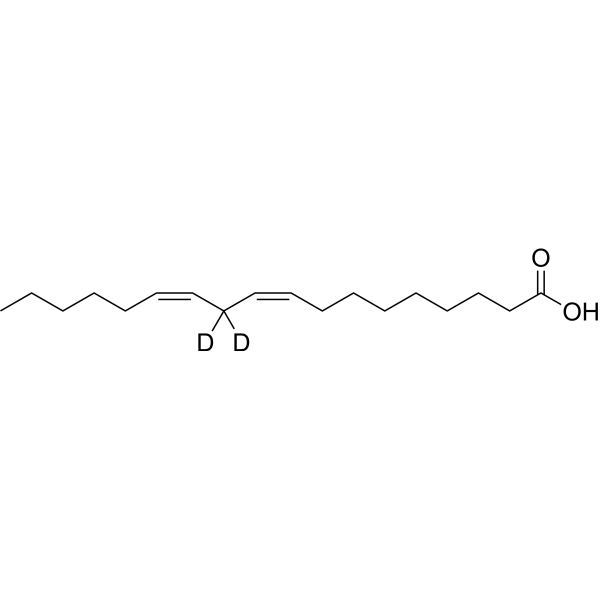
31447-29-7
| Name | Linoleic acid-d2 |
|---|
| Description | Linoleic Acid-d2 is the deuterium labeled Linoleic acid. Linoleic acid is a common polyunsaturated (PUFA) found in plant-based oils, nuts and seeds. Linoleic acid is a part of membrane phospholipids, and functions as a structural component to maintain a certain level of membrane fluidity of the transdermal water barrier of the epidermis. Linoleic acid induces red blood cells and hemoglobin damage via oxidative mechanism[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
[2]. Jay Whelan. Linoleic Acid. Adv Nutr. 2013 May; 4(3): 311–312. |
| Molecular Formula | C18H30D2O2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 282.46 |