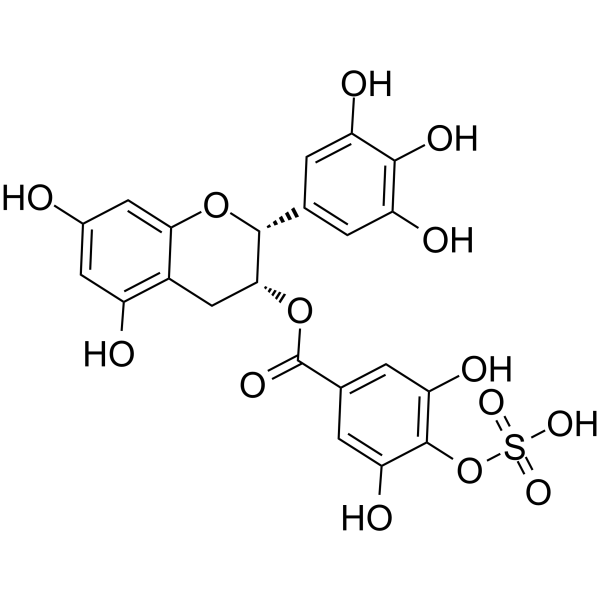
| Description |
EGCG-4″-sulfate is a major polyphenol in green tea, which can inhibit cell proliferation and induce cell apoptosis. (-)-Epigallocatechin Gallate sulfate inhibits glutamate dehydrogenase 1/2 (GDH1/2, GLUD1/2) activity. EGCG-4″-sulfate has a potent anticancer, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties against various types of cancers such as colorectal cancer, myeloid leukemia, thyroid carcinoma[1][2][3][4].
|
| In Vitro |
EGCG-4″-sulfate (10-60 μM) inhibits the growth of FB-2 and WRO cells in a dose-dependent manner[1]. EGCG-4″-sulfate (10-60 μM, 0-24 h) reduces cyclin D1 and phosphorylation of AKT and ERK1/2, and increases p21 and p53 expression[1]. EGCG-4″-sulfate (10-60 μM, 12 h) reduces cell motility and migration[1]. EGCG-4″-sulfate (0-20 μM, 0-20 min approximately) inhibits GLUD1/2 and IDH1 activity in a concentration and time-dependent way (biochemical assays)[2]. EGCG-4″-sulfate (0-35 μg/mL, 24-72 h) inhibits the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells (LoVo, SW480, HT-29, HCT-8 cells), increases cell apoptosis and blocks cells at the G0/G1 phase[3]. EGCG-4″-sulfate (30 μM, 3-24 h) suppresses the expression of COX-2 and mPGES-1 mRNAs, prostaglandin E2 production in LPS-induced osteoblasts[4]. Cell Proliferation Assay[1] Cell Line: FB-2 and WRO cells (serum-starved for 48h) Concentration: 10, 40, 60 μM. Incubation Time: 4 days Result: Inhibited basal cell proliferation (40% in FB-2 and 35% in WRO) at 10 μM, inhibited cell number (by 68% to 73%) at 40 and 60 μM). Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: FB-2 cells Concentration: 10, 40, 60 μM. Incubation Time: 24 h Result: Reduced cyclin D1 level, phosphorylation of AKT and ERK1/2. Induced the expression of p21 and p53, and E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Vimentin and α5-integrin. Cell Migration Assay [1] Cell Line: FB-2 and WRO cells (serum-starved for 48h) Concentration: 10, 40, 60 μM. Incubation Time: 12 h Result: Reduced migration activity in FB-2 and WRO cells. RT-PCR[4] Cell Line: Mouse primary osteoblasts (1 ng/ml LPS-treated) Concentration: 30 μM Incubation Time: 3, 6, 12, 24 h Result: Suppressed the LPS-induced expression of COX-2 and mPGES-1 mRNAs, prostaglandin E2 production.
|
| In Vivo |
EGCG-4″-sulfate (Intragastrical administration, 5-20 mg/kg, once daily for 14 days, orthotopic transplant model) decreases tumors growth[3]. EGCG-4″-sulfate (Injected into the mouse lower gingiva, a single dose of 0.5 mg/mouse, experimental periodontitis model) decreases inhibits the LPS-induced loss of bone mineral density (BMD)[3]. Animal Model: Orthotopic transplant BALB/c nude mice model[3] Dosage: 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg, once daily for 14 days. Administration: Intragastrical administration. Result: Inhibited tumors growth with no liver or lung metastases. Animal Model: Model of experimental periodontitis, LPS (25 μg/mouse)[4] Dosage: 0.5 mg/mouse, a single dose. Administration: Injected into the mouse lower gingiva Result: Inhibited the LPS-induced loss of bone mineral density (BMD) in mice.
|