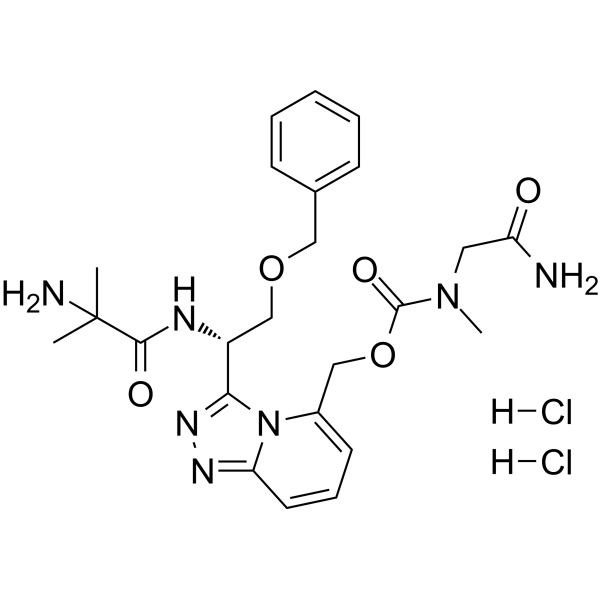
1469750-46-6
| Name | BMS-604992 dihydrochloride |
|---|
| Description | BMS-604992 (EX-1314) dihydrochloride is a selective, orally active small-molecule growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) agonist. BMS-604992 dihydrochloride demonstrates high-affinity binding (ki=2.3 nM) and potent functional activity (EC50=0.4 nM). BMS-604992 dihydrochloride can stimulate food intake in rodents[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
EC50: 0.4 nM (GHSR), Ki: 2.3 nM (GHSR)[1] |
| In Vitro | BMS-604992 exhibits high-affinity binding (Ki=2.3 nM) and potent functional activity (EC50=0.4 nM) for ghrelin receptor[1]. |
| In Vivo | BMS-604992 (500 μg/kg; i.p.; 5 minutes) results in a significant increase in gastric emptying compared with vehicle-treated mice[1]. BMS-604992 (1~1000 mg/kg; p.o.; 1 hour) Shows a dose-linear increase in plasma concentrations at the 1 hour time point and elicits a dose-responsive increase in food intake relative to vehicle-treated controls, with a minimum effective dose of approximately 10 mg/kg[1]. BMS-604992 (300 mg/kg; p.o.; 5~20 minutes) produces a significant difference at the 5 minutes time point[1]. BMS-604992 (500 μg/kg; i.p.; 4 hours) increases food intake approximately 2-fold compared with vehicle-treated controls[1]. Animal Model: C57BL/6 mice Dosage: 500 μg/kg Administration: I.p.; 5 minutes Result: Resulted in a significant increase in gastric emptying compared with vehicle-treated mice. Animal Model: C57BL/6 mice Dosage: 1~1000 mg/kg Administration: P.o.; 1 hour Result: Showed a dose-linear increase in plasma concentrations at the 1 hour time point and elicited a dose-responsive increase in food intake relative to vehicle-treated controls, with a minimum effective dose of approximately 10 mg/kg. Animal Model: SD rat Dosage: 300 mg/kg Administration: P.o.; 5~20 minutes Result: Observed a significant difference at the 5 minutes time point. Animal Model: Male GhrR KO and WT mice Dosage: 500 μg/kg Administration: I.p.; 4 hours Result: Increased food intake approximately 2-fold compared with vehicle-treated controls. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C24H33Cl2N7O5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 570.47 |