1228690-19-4
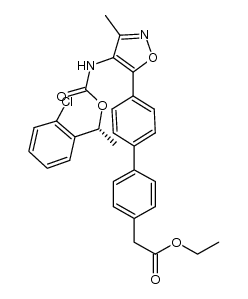
| Name | 2-[4-[4-[4-[[(1R)-1-(2-chlorophenyl)ethoxy]carbonylamino]-3-methyl-1,2-oxazol-5-yl]phenyl]phenyl]acetic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(4'-{4-[(R)-1-(2-Chloro-phenyl)-ethoxycarbonylamino]-3-methyl-isoxazol-5-yl}-biphenyl-4-yl)-acetic acid
UNII-CEO54NH393 CS-1013 (R)-2-(4'-(4-((1-(2-chlorophenyl)ethoxy)carbonylamino)-3-methylisoxazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)acetic acid 2-(4-{4-[4-({[(1R)-1-(2-chlorophenyl)ethoxy]carbonyl}amino)-3-methyl-1,2-oxazol-5-yl]phenyl}phenyl)acetic acid AM-966 AM966||AM-966 AM966 |
| Description | AM966 is a high affinity, selective, oral LPA1-antagonist, inhibits LPA-stimulated intracellular calcium release (IC50=17 nM). |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
LPA1[1] |
| In Vitro | AM966 is a potent, selective, orally bioavailable LPA1 receptor antagonist. AM966 inhibits LPA1-mediated chemotaxis of human A2058 melanoma cells (IC50=138±43 nM), IMR-90 human lung fibroblasts (IC50=182±86 nM) and CHO mLPA1 cells (IC50=469±54 nM)[1]. LPA-induced ERK1/2 activation is completely blocked by AM966 (100 nM), which selectively antagonizes LPA1 over LPA2-5, with an IC50 value of 3.8±0.4 nM. Pre-treatment with AM966 (100 nM) completely blocks ERK1/2 phosphorylation induced by either amitriptyline or mianserin[2]. |
| In Vivo | AM966 (30 mg/kg, BID) reduces vascular leakage, inflammation and lung injury and inflammation in a 3 day bleomycin model. AM966 inhibits lung fibrosis, maintains mouse body weight and decreases lung inflammation 14 days after bleomycin lung injury. AM966 reduces vascular leakage, tissue injury and pro-fibrotic cytokine production in the 14 day bleomycin study. AM966 demonstrates greater efficacy compared to pirfenidone in the 14 day bleomycin model. AM966 decreases mortality and fibrosis at late time points after bleomycin injury[1]. |
| Cell Assay | CHO-K1 cells are grown to 80% confluency in 12-well plates, serum-starved for 24 h and incubated in serum-free medium with AM966. After 21 h, [3H]thymidine (0.5 μCi/well) is added and the incubation is continued for 3 h. The medium is then removed, and the cells are placed on ice and washed twice with 1 mL of ice-cold PBS containing 5% trichloroacetic acid. Cells are solubilized and [3H]thymidine incorporation is determined by liquid scintillation counting. Assays are performed in triplicate[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] The oral exposure of AM966 is determined in fasted mice. Animals received AM966 (10 mg/kg) in vehicle (water) by oral gavage and are then killed by CO2 inhalation at 1, 2, 4, 8 and 24 h post dose (n=2 animals per time point for each test compound). Blood (approximately 300 µL) is collected via cardiac puncture into EDTA-containing tubes and centrifuged at 1450×g for 10 min. The plasma is removed and analysed for AM966 content by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LCMS). Briefly, known amounts of AM966 are added to thawed mouse plasma to yield a concentration range from 0.8 to 4000 ng/mL. Mouse plasma samples are precipitated using acetonitrile (1:4, v:v) containing the internal standard buspirone. A 10 µL aliquot of the analyte mixture is injected using a Leap PAL autosampler. Analyses are performed using an Agilent Zorbax SB-C8 column (2.1×50 mm; 5 µm) linked to a Shimadzu LC-10AD VP with SCL-10A VP system controller. Tandem mass spectrometric detection is carried out on a PE Sciex API3200 in the positive ion mode (ESI) by multiple reaction monitoring. The calibration curves are constructed by plotting the peak-area ratio of analysed peaks against known concentrations. The lower limit of quantitation is 0.8 ng/mL. The data are subjected to linear regression analysis with 1/x2weighting. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C27H23ClN2O5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 490.93500 |
| Exact Mass | 490.13000 |
| PSA | 105.15000 |
| LogP | 6.92080 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
|
~% 
1228690-19-4 |
| Literature: AMIRA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. Patent: US2010/152257 A1, 2010 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 23-24 ; US 20100152257 A1 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |