Myristoyl coenzyme A lithium salt
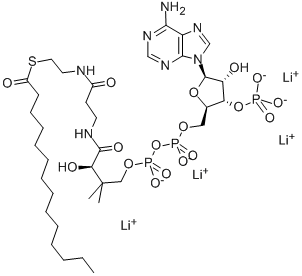
Myristoyl coenzyme A lithium salt structure
|
Common Name | Myristoyl coenzyme A lithium salt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 187100-75-0 | Molecular Weight | 1001.62 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C35H58Li4N7O17P3S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Myristoyl coenzyme A lithium saltMyristoyl coenzyme A lithium is lithium-labeled myristoylated coenzyme A (CoA). Myristoylation is an essential process in viruses and is generally controlled by N-myristoyltransferase (NMT). And NMT is more active in colon epithelial tumors than in normal cells. Reduced Ccoenzyme A (CoA) is known to be a key regulator of NMT activity, whereas oxidized CoA does not allow NMT to promote myristoylation. Myristoyl coenzyme A blocks the demyristoylation process and has potential anticancer and antiviral mechanisms. |
| Name | MYRISTOYL COENZYME A C14:0 LITHIUM SALT |
|---|
| Description | Myristoyl coenzyme A lithium is lithium-labeled myristoylated coenzyme A (CoA). Myristoylation is an essential process in viruses and is generally controlled by N-myristoyltransferase (NMT). And NMT is more active in colon epithelial tumors than in normal cells. Reduced Ccoenzyme A (CoA) is known to be a key regulator of NMT activity, whereas oxidized CoA does not allow NMT to promote myristoylation. Myristoyl coenzyme A blocks the demyristoylation process and has potential anticancer and antiviral mechanisms. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C35H58Li4N7O17P3S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 1001.62 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Functional significance of myristoyl moiety in N-myristoyl proteins.
Meth. Enzymol. 250 , 405, (1995)
|
|
|
Fatty acid elongation in yeast--biochemical characteristics of the enzyme system and isolation of elongation-defective mutants.
Eur. J. Biochem. 252 , 477-485, (1998) Elongation of long-chain fatty acids was investigated in yeast mutants lacking endogenous de novo fatty acid synthesis. In this background, in vitro fatty acid elongation was dependent strictly on the... |
|
|
Modification of GTP-activated calcium translocation by fatty acyl-CoA esters. Evidence for a GTP-induced prefusion event.
J. Biol. Chem. 269 , 31607, (1994) A sensitive and specific GTP-activated Ca2+ translocation process induces rapid Ca2+ movements within cells and appears to reflect G protein-induced membrane fusion or junctional communication between... |