Amphotericin B trihydrate Suppliers
Total count: 1
- China(Mainland)
- Contact: Yang
- Phone: 0086-021-52280163
- Email: sales@echemcloud.com
- Website: http://www.echemcloud.com
- Product Name: Amphotericin B trihydrate
- Updated Date: 2024-07-15 12:30:36
- Purity: 98.0%
- More information
Inquiry
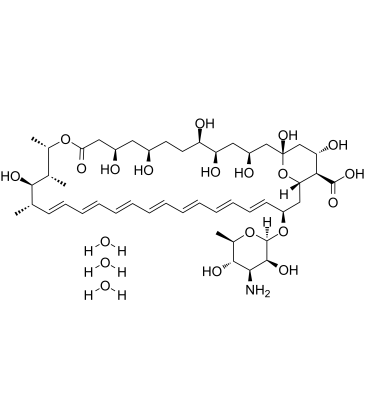
Amphotericin B trihydrate
- CAS Number: 1202017-46-6
- Molecular Formula: C47H79NO20
- Molecular Weight: 978.12
Related product suppliers
Check more product suppliers