Acceleration of the refolding of Arc repressor by nucleic acids and other polyanions.
D Rentzeperis, T Jonsson, R T Sauer
Index: Nat. Struct. Biol. 6(6) , 569-73, (1999)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The refolding rate of the Arc repressor dimer can be accelerated 30-fold or more by negatively charged polymers including single-stranded and double-stranded DNA, RNA, and polyvinylsulfate but not by neutral or positively charged polymers. The salt-dependence of the polyanion-mediated process and mutant studies indicate that electrostatic interactions are important in the rate acceleration. Urea-dependence studies suggest that Arc is relatively unstructured in the transition state for polyanion-stimulated refolding. At low ionic strength, the observed kinetics of refolding are consistent with a model in which denatured Arc monomers bind rapidly and nonspecifically to the polyanion and complete folding in the bound state.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
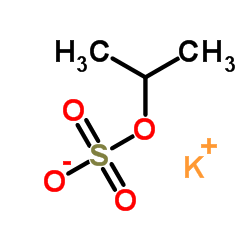 |
Poly(vinyl sulfate) potassium salt
CAS:26182-60-5 |
C3H7KO4S |
|
Binding of ethidium to the nucleosome core particle. 2. Inte...
1991-06-11 [Biochemistry 30 , 5644, (1991)] |
|
Apparent specificity of bovine seminal ribonucleases can dep...
1992-02-01 [Biochem. Int. 26(1) , 125-33, (1992)] |
|
A mycelium with polyelectrolyte complex-bunched hyphae: prep...
2007-04-15 [Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 56(1-2) , 155-60, (2007)] |
|
Coulombic and noncoulombic effect of polyanions on cytochrom...
1998-09-01 [Biopolymers 46(3) , 145-54, (1998)] |
|
Light scattering study of complex formation between protein ...
2007-04-15 [Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 56(1-2) , 142-8, (2007)] |