Impact of linker strain and flexibility in the design of a fragment-based inhibitor.
Suhman Chung, Jared B Parker, Mario Bianchet, L Mario Amzel, James T Stivers
Index: Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 , 407-13, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The linking together of molecular fragments that bind to adjacent sites on an enzyme can lead to high-affinity inhibitors. Ideally, this strategy would use linkers that do not perturb the optimal binding geometries of the fragments and do not have excessive conformational flexibility that would increase the entropic penalty of binding. In reality, these aims are seldom realized owing to limitations in linker chemistry. Here we systematically explore the energetic and structural effects of rigid and flexible linkers on the binding of a fragment-based inhibitor of human uracil DNA glycosylase. Analysis of the free energies of binding in combination with cocrystal structures shows that the flexibility and strain of a given linker can have a substantial impact on binding affinity even when the binding fragments are optimally positioned. Such effects are not apparent from inspection of structures and underscore the importance of linker optimization in fragment-based drug discovery efforts.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
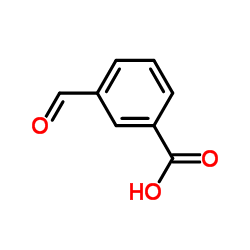 |
3-Formylbenzoic acid
CAS:619-21-6 |
C8H6O3 |
|
Novel styrylbenzene derivatives for detecting amyloid deposi...
2014-09-25 [Clin. Chim. Acta 436 , 27-34, (2014)] |
|
Synthesis and evaluation of 3-(dihydroxyboryl)benzoic acids ...
2009-10-08 [J. Med. Chem. 52 , 6097-106, (2009)] |
|
Synthesis of Alicyclic-lactams via the Ugi Reaction on a Sol...
[Lett. Org. Chem. 1(3) , 215-20, (2004)] |
|
Synthesis, binding properties and self-functionalization of ...
[J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 8 , 574-77, (1991)] |
|
Synthesis of 4-amino-6-(hetero)arylalkylamino-1,2,4-triazolo...
2003-12-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 11(24) , 5509-18, (2003)] |