FTIR study of the photoisomerization processes in the 13-cis and all-trans forms of Anabaena sensory rhodopsin at 77 K.
Akira Kawanabe, Yuji Furutani, Kwang-Hwan Jung, Hideki Kandori
Index: Biochemistry 45(14) , 4362-70, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Archaeal-type rhodopsins can accommodate either all-trans- or 13-cis,15-syn-retinal in their chromophore binding site in the dark, but only the former isomer is functionally important. In contrast, Anabaena sensory rhodopsin (ASR), an archaeal-type rhodopsin found in eubacteria, exhibits a photochromic interconversion of both forms, suggesting that ASR functions as a photosensor which interacts with its 14 kDa soluble transducer differently in the all-trans and 13-cis,15-syn forms. In this study, we applied low-temperature Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy to the 13-cis,15-syn form of ASR (13C-ASR) at 77 K and compared the local structure around the chromophore and its structural changes upon retinal photoisomerization with those of the all-trans form (AT-ASR) [Furutani, Y., Kawanabe, A., Jung, K. H., and Kandori, H. (2005) Biochemistry 44, 12287-12296]. By use of [zeta-15N]lysine-labeled ASR, we identified the N-D stretching vibrations of the Schiff base (in D2O) at 2165 cm(-1) for 13C-ASR and at 2163 and 2125 cm(-1) for AT-ASR. The frequencies indicate strong hydrogen bonds of the Schiff base with a water molecule for both 13C-ASR and AT-ASR. In contrast, the N-D stretching vibration appears at 2351 cm(-1) and at 2483 cm(-1) for the K states of 13C-ASR (13C-ASR(K)) and AT-ASR (AT-ASR(K)), respectively, indicating that the Schiff base still forms a hydrogen bond in 13C-ASR(K). Rotational motion of the Schiff base upon retinal isomerization is probably smaller for 13C-ASR than for AT-ASR, the latter altering hydrogen bonding of the Schiff base similar to bacteriorhodopsin (BR), a light-driven proton pump. Appearance of several hydrogen-out-of-plane vibrations and amide I vibrations in 13C-ASR(K), but not in AT-ASR(K), suggests that structural changes are distributed widely along the polyene chain for 13C-ASR. On the other hand, retinal photoisomerization in AT-ASR breaks the hydrogen bond of the Schiff base, and localized structural changes in the Schiff base region are induced.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
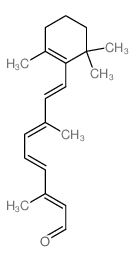 |
Retinal, 13-cis
CAS:472-86-6 |
C20H28O |
|
HEK293S cells have functional retinoid processing machinery.
2002-06-01 [J. Gen. Physiol. 119(6) , 593-612, (2002)] |
|
Probing human red cone opsin activity with retinal analogues...
2011-03-25 [J. Nat. Prod. 74 , 391-4, (2011)] |
|
Cantilever-based sensor for the detection of different chrom...
2007-06-15 [Anal. Chem. 79(12) , 4702-8, (2007)] |
|
In vivo treatment with CPT-11 leads to differentiation of ne...
2004-05-01 [Cancer Res. 64(9) , 3223-9, (2004)] |
|
Effect of retinoids on the growth of squamous cell carcinoma...
1986-01-01 [Am. J. Otolaryngol. 7(1) , 55-7, (1986)] |