Dioxygenolytic cleavage of aryl ether bonds: 1,2-dihydro-1,2-dihydroxy-4-carboxybenzophenone as evidence for initial 1,2-dioxygenation in 3- and 4-carboxy biphenyl ether degradation.
K H Engesser, W Fietz, P Fischer, P Schulte, H J Knackmuss
Index: FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 57(3) , 317-21, (1990)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A bacterial strain, Pseudomonas sp. POB 310, was enriched with 4-carboxy biphenyl ether as sole source of carbon and energy. Resting cells of POB 310 co-oxidize a substrate analogue, 4-carboxybenzophenone, yielding 1,2-dihydro-1,2-dihydroxy-4-carboxy-benzophenone. The ether bond of 3- and 4-carboxy biphenyl ether is cleaved analogously by initial 1,2-dioxygenation, yielding a hemiacetal which is hydrolysed to protocatechuate and phenol. These intermediates are degraded via an ortho and meta pathway, respectively. Alternative 2,3- and 3,4-dioxygenation can be ruled out as triggering steps in carboxy biphenyl ether degradation.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
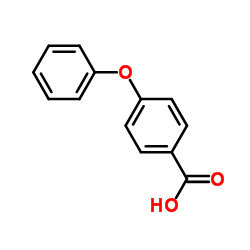 |
4-Phenoxybenzoic acid
CAS:2215-77-2 |
C13H10O3 |
|
Effects of amino acids on the amidation of polyaromatic carb...
2001-08-01 [Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 65(8) , 1761-5, (2001)] |
|
Microarray immunoassay for phenoxybenzoic acid using polymer...
2005-11-01 [Anal. Chem. 77(21) , 6864-73, (2005)] |
|
Structure--activity relationships of azasugar-based MMP/ADAM...
2003-08-18 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 13(16) , 2737-40, (2003)] |
|
Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of the gene enc...
1995-01-01 [Arch. Microbiol. 163(1) , 35-41, (1995)] |
|
Prooxidant and antioxidant action of 4-(4-phenoxybenzoyl)ben...
2004-04-05 [Biopolymers 73(5) , 631-9, (2004)] |