Ultrasensitive immunoassay of 7-aminoclonazepam in human urine based on CdTe nanoparticle bioconjugations by fabricated microfluidic chip
Wei Chen, Chifang Peng, Zhengyue Jin, Ruirui Qiao, Wuyang Wang, Shuifang Zhu, Libing Wang, Qinhui Jin, Chuanlai Xu
Index: Biosens. Bioelectron. 24(7) , 2051-6, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The present paper described a rapid and ultrasensitive detection method using a microfluidic chip for analyzing 7-aminoclonazepam (7-ACZP) residues in human urine. A microfluidic chip-based immunoassay with laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) detection based on the water-soluble denatured bovine serum albumin (dBSA)-coated CdTe quantum dots (QDs) was prepared for the ultrasensitive detection of 7-ACZP. The whole procedure including the chip and the control software was designed and constructed in our own laboratory. The detection of 7-ACZP could be completed within 5min. The results demonstrated that under the optima conditions, 7-ACZP residues could be detected with a precision of 5% relative standard deviation (RSD), and the linear range and the limit of detection (LOD) for 7-ACZP were 1.1–60.1 and 0.021ngmL−1, respectively. This method was compared with ELISA and showed a good correlation. This microfluidic chip with LIF detection was applied to the determination of 7-ACZP residues in positive human urine samples, and the results were confirmed by high-performance liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). This ultrasensitive detection technique was proved to be practical for clinical use.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
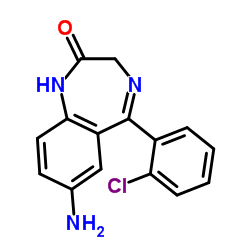 |
7-Aminoclonazepam(CRM)
CAS:4959-17-5 |
C15H12ClN3O |
|
Extraction and analysis of clonazepam and 7-aminoclonazepam ...
2007-03-02 [Forensic Sci. Int. 166(2-3) , 209-17, (2007)] |
|
A highly sensitive method for the determination of 7-aminoni...
2009-07-01 [Biomed. Chromatogr. 23(7) , 740-4, (2009)] |
|
Simultaneous determination and quantification of 12 benzodia...
2010-01-01 [Methods Mol. Biol. 603 , 107-19, (2010)] |
|
LC-MS/MS analysis of 13 benzodiazepines and metabolites in u...
2010-01-01 [Methods Mol. Biol. 603 , 89-105, (2010)] |
|
Prolonged excretion of 7-aminoclonazepam in urine after repe...
2012-10-10 [Forensic Sci. Int. 222(1-3) , e33-5, (2012)] |