Adenylate cyclase from sea urchin eggs is positively and negatively regulated by D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptors.
V Carginale, A Capasso, L Madonna, L Borrelli, E Parisi
Index: Exp. Cell Res. 203(2) , 491-4, (1992)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The adenylate cyclase present in membranes prepared from sea urchin eggs is sensitive to dopamine stimulation. The receptor sites coupled to sea urchin adenylate cyclase were characterized by means of specific agonists and antagonists. The D-1 dopamine agonist SKF-38393 was able to stimulate enzyme activity, while the two D-1 dopamine antagonists, SCH-23390 and SKF-83566, suppressed the stimulatory effect of dopamine. In addition, the D-2 dopamine agonists, PPHT and metergoline, brought about a dose-dependent inhibition of dopamine-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity. These data show that: (i) in sea urchin eggs adenylate cyclase is regulated by dopamine receptors; (ii) these receptors share characteristics with D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptors present in the mammalian brain.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
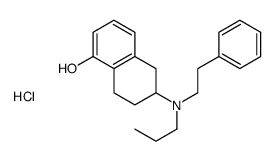 |
(+/-)-PPHT HYDROCHLORIDE (N-0434) POTENT D2 DOPAMINE RE
CAS:71787-90-1 |
C21H28ClNO |
|
Differential effects of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor agonists...
1995-04-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 273 , 40, (1995)] |
|
Multiple fluorescent ligands for dopamine receptors. I. Phar...
1991-05-03 [Brain Res. 547(2) , 199-207, (1991)] |
|
Relations between the extracellular concentrations of cholin...
1997-09-01 [J. Neurochem. 69(3) , 1246-51, (1997)] |
|
Biphasic effects of dopamine agonist N-0434 on locomotor beh...
1993-04-01 [Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 44(4) , 865-8, (1993)] |
|
Transient loss of dopamine autoreceptor control in the prese...
1996-12-01 [Life Sci. 59(21) , PL317-24, (1996)] |