Two biologically active isomers of dihydroouabain isolated from a commercial preparation.
H M Qazzaz, M A El-Masri, N J Stolowich, R Valdes
Index: Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1472(3) , 486-97, (1999)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Ouabain is a plant-derived cardiac glycoside that inhibits the catalytic activity of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase (sodium pump; NKA). Dihydroouabain, a derivative of ouabain with a reduced lactone ring, is commonly used as a sodium pump antagonist. It has been assumed that commercially available dihydroouabain is homogeneous. We now report that preparations of dihydroouabain contain two components each with a different potency for inhibition of sodium pump activity. We used reverse-phase HPLC chromatography, UV spectrophotometry, electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (ESI-MS), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and two independent bioassays to characterize these compounds. The two dihydroouabain fractions (Dho-A and Dho-B) resolved by 3 min chromatographically, had UV absorbance maxima at 196 nm, and comprised 37% and 63% of the stock dihydroouabain, respectively. The molar potency of each component for inhibition of NKA from porcine cerebral cortex differed by 4. 4-fold (Dho-A, IC(50) = 7.13 +/- 0.8 microM; Dho-B, IC(50) = 1.63 +/- 0.12 microM). The relative potencies were 9% and 40% of those of ouabain, respectively. A similar pattern for phosphorylation of NKA was observed. Mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) and fragmentation patterns are consistent with Dho-A and Dho-B being isomers of identical molecular mass (587 Da) and each with six hydroxyl groups, a deoxyhexose sugar moiety and a lactone ring. Furthermore, NMR spectroscopy revealed structural differences between Dho-A and Dho-B by displaying noticeably different chemical shifts at only two groups of proton resonances assigned to H-21 and H-22. The ESI-MS and NMR results confirm the presence of the isomerism at C20 of the lactone ring. Our results demonstrate the existence of two molecular forms of dihydroouabain, each with a different biological potency. These findings underscore the importance of characterizing the purity of dihydroouabain commercial preparations. It also provides possible molecular models for investigating the metabolism of endogenous ouabain-like factors recently reported in mammals.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
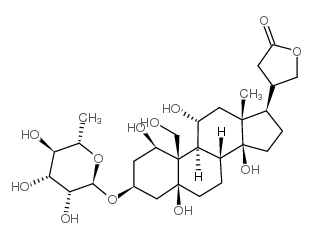 |
dihydroouabain
CAS:1183-35-3 |
C29H46O12 |
|
Sodium-potassium-ATPase electrogenicity in cerebral precapil...
2000-07-01 [Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 279(1) , H351-60, (2000)] |
|
Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase inhibition upregulates NMDA-evoked current...
2012-08-01 [Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 26(4) , 503-12, (2012)] |
|
Contribution of cytosolic ionic and energetic milieu change ...
1998-01-01 [J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 31(1) , 146-56, (1998)] |
|
Isoform-specific function and distribution of Na/K pumps in ...
2000-11-15 [J. Membr. Biol. 178(2) , 89-101, (2000)] |
|
Novel form of LTD induced by transient, partial inhibition o...
2004-01-01 [J. Neurophysiol. 91(1) , 239-47, (2004)] |