Effect of Isoenzyme Selective Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors on the Proliferation of Murine Thymus and Spleen Cells
K.H. Banner, B. Bertin, I. Moodley, C.P. Page
Index: Pulm. Pharmacol. 9(1) , 35-41, (1996)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The effects of isoenzyme selective phosphodiesterase inhibitors on mitogen-stimulated proliferation of murine thymus and spleen cells was determined. The type 4 phosphodiesterase inhibitors, (rolipram, RO 20-1724 and denbufylline) and the mixed type 3/4 inhibitors, (zardaverine and benzafentrine) produced a concentration-related inhibition of mitogen stimulated thymus and spleen cell proliferation. Combined addition of the type 4 inhibitor, rolipram and the type 3 inhibitor, SK&F 94836 had no antiproliferative effect additional to that of rolipram alone. The thymus cells were more sensitive to the type 4 inhibitors than the spleen cells. The type 3 phosphodiesterase inhibitor, SK&F 94836 significantly inhibited cell proliferation, but only at high concentrations. The type 1 (vinpocetine) and the type 5 (zaprinast) phosphodiesterase inhibitor had no significant effect on proliferation. These results suggest that thymus and to a lesser extent spleen cell proliferation is dependent on the activity of the type 4 phosphodiesterase isoenzyme.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
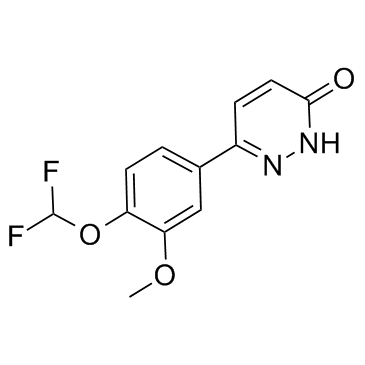 |
Zardaverine
CAS:101975-10-4 |
C12H10F2N2O3 |
|
Uncovering caffeine's adenosine A2A receptor inverse agonism...
2014-11-21 [ACS Chem. Biol. 9(11) , 2496-501, (2014)] |
|
Dopamine receptors D3 and D5 regulate CD4(+)T-cell activatio...
2015-07-15 [J. Neuroimmunol. 284 , 18-29, (2015)] |
|
Phenotype-based screening of mechanistically annotated compo...
2006-08-01 [J. Biomol. Screen. 11(5) , 457-68, (2006)] |
|
The specific type III and IV phosphodiesterase inhibitor zar...
1993-01-05 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 230(1) , 9-14, (1993)] |
|
Crystal structure of phosphodiesterase 4D and inhibitor comp...
2002-10-23 [FEBS Lett. 530(1-3) , 53-8, (2002)] |