Development and design of specific inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme.
D W Cushman, H S Cheung, E F Sabo, M A Ondetti
Index: Am. J. Cardiol. 49(6) , 1390-4, (1982)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Captopril is a remarkably effective new antihypertensive drug designed and developed as a potent and specific inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme, a zinc metallopeptidase that participates in the synthesis of a hypertensive peptide, angiotensin II, and in the degradation of a hypotensive peptide, bradykinin. Earlier studies with a snake venom peptide (teprotride or SQ 20881) that could be administered only by injection demonstrated that specific inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme could be highly effective as antihypertensive drugs, and helped to clarify the specificity and mechanism of action of the enzyme. A hypothetical model of the active center of angiotensin-converting enzyme based on its presumed analogy to the well characterized zinc metallopeptidase carboxypeptidase A was used to guide logical sequential improvements of a weakly active prototype inhibitor that led eventually to the highly optimized structure of captopril. The hypothetical working model of the active site of angiotensin-converting enzyme used to develop captopril continues to provide a firm basis for development of new types of specific inhibitors of this biologically important enzyme.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
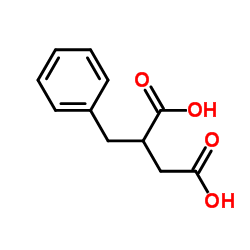 |
2-Benzylsuccinic acid
CAS:884-33-3 |
C11H12O4 |
|
Regulation of cytoplasmic tubulin carboxypeptidase activity ...
1996-03-01 [J. Cell. Biochem. 60(3) , 424-36, (1996)] |
|
Nerve injury evoked loss of latexin expression in spinal cor...
2011-01-01 [PLoS ONE 6(4) , e19270, (2011)] |
|
The three-dimensional structure of human procarboxypeptidase...
1997-12-01 [EMBO J. 16(23) , 6906-13, (1997)] |
|
Bacterial chemotactic oligopeptides and the intestinal mucos...
1989-07-01 [Gastroenterology 97(1) , 61-7, (1989)] |
|
[Design, synthesis and hypoglycemic activity of alpha-benzyl...
2009-05-01 [Yao Xue Xue Bao 44(5) , 491-5, (2009)] |