Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of novel arylfluoroquinolone antibacterial agents.
D T Chu, P B Fernandes, A K Claiborne, E Pihuleac, C W Nordeen, R E Maleczka, A G Pernet
Index: J. Med. Chem. 28 , 1558, (1985)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A series of novel arylfluoroquinolones has been prepared. These derivatives are characterized by having a fluorine atom at the 6-position, substituted amino groups at the 7-position, and substituted phenyl groups at the 1-position. Structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies indicate that the in vitro antibacterial potency is greatest when the 1-substituent is either p-fluorophenyl or p-hydroxyphenyl and the 7-substituent is either 1-piperazinyl, 4-methyl-1-piperazinyl, or 3-amino-1-pyrrolidinyl. The electronic and spatial properties of the 1-substituent, as well as the steric bulk, play important roles in the antimicrobial potency in this class of antibacterials. As a result of this study, compounds 45 and 41 were found to possess excellent in vitro potency and in vivo efficacy.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
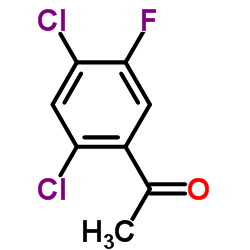 |
1-(2,4-Dichloro-5-fluorophenyl)ethanone
CAS:704-10-9 |
C8H5Cl2FO |
|
Synthesis of some halogen-containing 1,2,4-triazolo-1,3,4-th...
2001-08-01 [Il Farmaco 56(8) , 565-70, (2001)] |
|
[Zhongguo Yiyao Gongye Zazhi 25 , 296, (1994)] |
|
[Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 55 , 1311, (1990)] |
|
[J. Heterocycl. Chem. 25 , 927, (1988)] |
|
Eco-friendly synthesis of fluorine-containing pyrazoline der...
[ARKIVOC 1 , 123-29, (2004)] |