Whole genomic expression analysis of octachlorostyrene-induced chronic toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Seung Jun Kim, Se Young Choung
Index: Arch. Pharm. Res. 32(11) , 1585-92, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
In recent years, microarray technology has enabled the investigation of possible mechanisms the expression of genes related to toxic compounds. We used a C. elegans whole genome microarray to observe and evaluate the chronic toxicity of the free-living nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) after exposure to octachlorostyrene, (OCS), a by-product in the manufacture of many chlorinated hydrocarbons. In this study, we examined sublethal toxicity, egg hatching, and movement of octachlorostyrene over three generations using a nematode growth medium (NGM) agar plate. In the third generation, OCS affected the fecundity rate of C. elegans. Specifically, the number of worm and eggs decreased significantly to about 50% of control (p < 0.05). In microarray experiments, total RNA was isolated at 0, 2 and 3 generations following treatment of OCS, and hybridized to the microarray containing about 22,000 C. elegans genes. Dye swaps were performed. After data analysis, we identified a total of 1,294 genes that were differentially expressed through generations.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
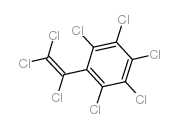 |
octachlorostyrene
CAS:29082-74-4 |
C8Cl8 |
|
Measuring nonpolar organic contaminant partitioning in three...
2012-04-15 [Sci. Total Environ. 423 , 125-31, (2012)] |
|
Organochlorine pesticides, octachlorostyrene, and mercury in...
1992-01-01 [Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 22(1) , 14-20, (1992)] |
|
The tissue distribution, metabolism, and excretion of octach...
1982-01-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 10(6) , 632-5, (1982)] |
|
Induction of liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 and associate...
1982-08-01 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 31(15) , 2523-9, (1982)] |
|
Induction of oxidative stress in human Chang liver cells by ...
2008-03-01 [Toxicol. In Vitro 22(2) , 367-75, (2008)] |