Importance of NF-kappaB in rheumatoid synovial tissues: in situ NF-kappaB expression and in vitro study using cultured synovial cells.
S Yamasaki, A Kawakami, T Nakashima, H Nakamura, M Kamachi, S Honda, Y Hirai, A Hida, H Ida, K Migita, Y Kawabe, T Koji, I Furuichi, T Aoyagi, K Eguchi
Index: Ann. Rheum. Dis. 60(7) , 678-84, (2001)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
To examine whether inhibition of NF-kappaB induces apoptosis of human synovial cells stimulated by tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha), interleukin 1beta (IL1beta), and anti-Fas monoclonal antibody (mAb).The expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), NF-kappaB, and the presence of apoptotic synovial cells were determined in synovial tissues. Apoptosis of cultured synovial cells was induced by inhibition of NF-kappaB nuclear translocation by Z-Leu-Leu-Leu-aldehyde (LLL-CHO). The activation of caspase-3 and expression of XIAP and cIAP2 in synovial cells in LLL-CHO induced apoptosis was also examined.Abundant PCNA+ synovial cells were found in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial tissue, though a few apoptotic synovial cells were also detected in the RA synovial tissues. Nuclear NF-kappaB was expressed in RA synovial cells. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay showed that treatment of cells with TNFalpha or IL1beta significantly stimulated nuclear NF-kappaB activity. A small number of apoptotic synovial cells expressing intracellular active caspase-3 were found after treatment of cells with LLL-CHO. Although treatment of RA synovial cells with TNFalpha or IL1beta alone did not induce apoptosis, apoptosis induced by LLL-CHO and caspase-3 activation were clearly enhanced in TNFalpha or IL1beta stimulated synovial cells compared with unstimulated synovial cells. Furthermore, induction of apoptosis of synovial cells with caspase-3 activation by anti-Fas mAb was clearly increased by LLL-CHO. The expression of cIAP2 and XIAP in synovial cells may not directly influence the sensitivity of synovial cells to apoptosis induced by LLL-CHO.The results suggest that NF-kappaB inhibition may be a potentially important therapeutic approach for RA by correcting the imbalance between apoptosis and proliferation of synovial cells in RA synovial tissue.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
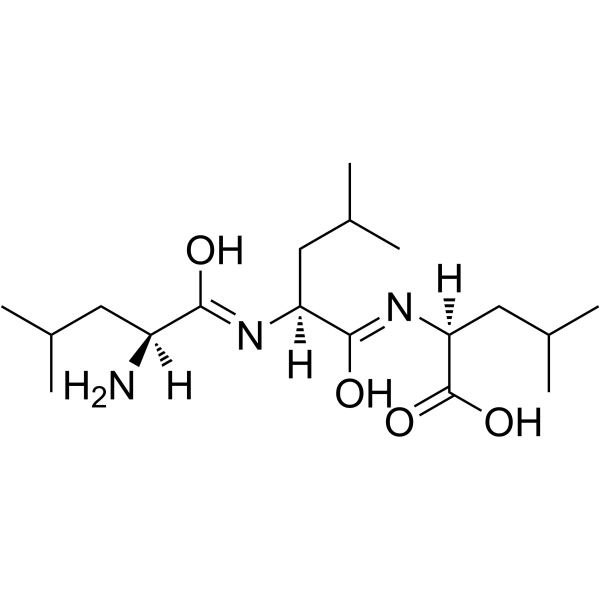 |
H-Leu-Leu-Leu-OH
CAS:10329-75-6 |
C18H35N3O4 |
|
Inhibition of brain tumor growth by intravenous poly (β-L-ma...
2010-10-19 [Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107 , 18143-18148, (2010)] |
|
Trileucine improves aerosol performance and stability of spr...
2008-01-01 [J. Pharm. Sci. 97 , 287-302, (2008)] |
|
Temozolomide delivery to tumor cells by a multifunctional na...
2010-11-01 [Pharm. Res. 27 , 2317-2329, (2010)] |
|
Critical roles for the COOH terminus of the Cu-ATPase ATP7B ...
2011-07-01 [Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 301 , G69-81, (2011)] |
|
Investigation of the adsorption mechanism of a peptide in re...
2009-05-01 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1216 , 3992-4004, (2009)] |