Electrolysis-mediated irreversible inactivation of lipoxygenase directed toward electroaffinity labelling.
T J Holmes, J L Vennerstrom, V John
Index: Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 123(1) , 156-62, (1984)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Irreversible inhibition of soybean lipoxygenase-1 (SL-1) was accomplished via a controlled potential oxidative electrolysis of 1,5-dihydroxynaphthalene (1,5-DHN) at +0.8 V vs SCE. The inactivation of SL-1 with this known inhibitor was greatly enhanced under these electrolytic conditions to which the enzyme itself was stable. Electrolyses were run at 0 degree C in a 0.05 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.0, using graphite cloth electrodes. The rate of inactivation was observed to be limited by and dependent on the anodic oxidation of 1,5-DHN. The non-oxidizable (at this potential) inhibitor indomethacin was shown to protect the enzyme from irreversible inactivation, however, an external nucleophile (2-mercaptoethanol) had little effect. These initial studies support the capability of such electrochemical methods for the site-specific covalent modification (affinity labelling) of lipoxygenase, and perhaps other enzymes.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
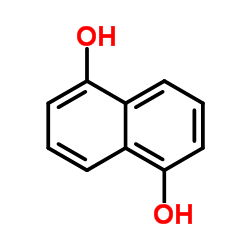 |
1,5-Dihydroxynaphthalene
CAS:83-56-7 |
C10H8O2 |
|
Effects of cyano-substituents on the molecular packing struc...
2014-09-24 [ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6(18) , 15774-82, (2014)] |
|
Selective antiproliferative activity of hydroxynaphthyl-beta...
2006-03-23 [J. Med. Chem. 49 , 1932-8, (2006)] |
|
Photooxidation of 1,5-dihydroxynaphthalene with iridium comp...
2011-06-01 [Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 10(6) , 895-903, (2011)] |
|
Flavonoids and related compounds as inhibition of arachidoni...
1980-10-01 [Prostaglandins 20(4) , 627-39, (1980)] |
|
Visible light-harvesting perylenebisimide-fullerene (C60) dy...
2012-04-18 [Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 48(31) , 3751-3, (2012)] |