Transacetylations to carbohydrates catalyzed by acetylxylan esterase in the presence of organic solvent.
Peter Biely, Ken K Y Wong, Ian D Suckling, Silvia Spániková
Index: Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1623 , 62-71, (2003)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Various conditions were applied to test the ability of acetylxylan esterase (AcXE) from Schizophyllum commune to catalyze acetyl group transfer to methyl beta-D-xylopyranoside (Me-beta-Xylp) and other carbohydrates. The best performance of the enzyme was observed in an n-hexane-vinyl acetate-sodium dioctylsulfosuccinate (DOSS)-water microemulsion at a molar water-detergent ratio (w(0)) of about 4-5. Although the enzyme was found to have a half-life of about 1 h in the system, more than 60% conversion of Me-beta-Xylp to acetylated derivatives was achieved. Under identical reaction conditions, the enzyme acetylated other carbohydrates such as methyl beta-D-cellobioside (Me-beta-Cel), cellotetraose, methyl beta-D-glucopyranoside (Me-beta-Glcp), 2-deoxy-D-glucose, D-mannose, beta-1,4-mannobiose, -mannopentaose, -mannohexaose, beta-1,4-xylobiose and -xylopentaose. This work is the first example of reverse reactions by an acetylxylan esterase and a carbohydrate esterase belonging to family 1.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
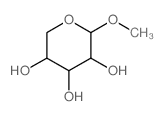 |
beta-D-Xylopyranoside, methyl
CAS:612-05-5 |
C6H12O5 |
|
Effects of inhibition of proteoglycan synthesis on the diffe...
1987-08-01 [J. Cell Biol. 105(2) , 1013-21, (1987)] |
|
Tetraisopropyldisiloxane-1,3-diyl as a versatile protecting ...
2012-05-15 [Carbohydr. Res. 353 , 92-5, (2012)] |
|
Synthesis of acylated methyl beta-D-xylopyranosides and thei...
1997-07-11 [Carbohydr. Res. 302(1-2) , 13-8, (1997)] |
|
Determination of sugar structures in solution from residual ...
2004-10-13 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126(40) , 13100-10, (2004)] |
|
Mode of action of acetylxylan esterase from Streptomyces liv...
2003-07-23 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1622(2) , 82-8, (2003)] |