An easy access to halide ion-catalytic alpha-glycosylation using carbon tetrabromide and triphenylphosphine as multifunctional reagents.
Yuko Shingu, Yoshihiro Nishida, Hirofumi Dohi, Kazukiyo Kobayashi
Index: Org. Biomol. Chem. 1(14) , 2518-21, (2003)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The reaction of a 2-O-benzyl-1-hydroxy sugar with CBr4 and Ph3P generates a glycosyl bromide in situ, which is coupled with an acceptor alcohol in the presence of N,N-tetramethylurea to afford an alpha-glycosyl product virtually quantitatively. In a proposed pathway, the reagent combination plays multiple roles such as the generation of a glycosyl donor, the activation of glycosylation, and the dehydration of the reaction system. These roles allow a simple alpha-glycosylation to be performed without special attention to dehydration. Various alpha-glycosyl (D-gluco-, D-galacto- and L-fuco-) products including glycosyl glycerols and cholesterols have been prepared with this method.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
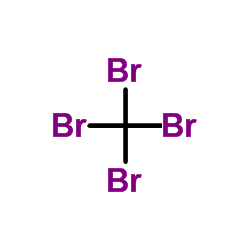 |
Tetrabromomethane
CAS:558-13-4 |
CBr4 |
|
Kinetic and mechanistic examinations of reductive transforma...
2007-02-01 [Water Res. 41(4) , 875-83, (2007)] |
|
Structures of bromoalkanes' photodissociation in solution by...
2002-10-01 [Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99(20) , 12556-61, (2002)] |
|
A strategy for sequence control in vinyl polymers via iterat...
2016-01-01 [Nat. Commun. 7 , 11064, (2016)] |
|
Photodissociation dynamics of CBr4 at 267 nm by means of ion...
2006-10-07 [J. Chem. Phys. 125(13) , 133311, (2006)] |
|
Long term puzzles of the CH and CD energetics and related ph...
2016-01-21 [Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18 , 1797-806, (2016)] |