GABAA/Benzodiazepine receptor binding in patients with schizophrenia using [11C]Ro15-4513, a radioligand with relatively high affinity for alpha5 subunit.
Yoshiyuki Asai, Akihiro Takano, Hiroshi Ito, Yoshiro Okubo, Masato Matsuura, Akihiko Otsuka, Hidehiko Takahashi, Tomomichi Ando, Shigeo Ito, Ryosuke Arakawa, Kunihiko Asai, Tetsuya Suhara
Index: Schizophr. Res. 99(1-3) , 333-40, (2008)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Dysfunction of the GABA system is considered to play a role in the pathology of schizophrenia. Individual subunits of GABA(A)/Benzodiazepine (BZ) receptor complex have been revealed to have different functional properties. alpha5 subunit was reported to be related to learning and memory. Changes of alpha5 subunit in schizophrenia were reported in postmortem studies, but the results were inconsistent. In this study, we examined GABA(A)/BZ receptor using [(11)C]Ro15-4513, which has relatively high affinity for alpha5 subunit, and its relation to clinical symptoms in patients with schizophrenia. [(11)C]Ro15-4513 bindings of 11 patients with schizophrenia (6 drug-naïve and 5 drug-free) were compared with those of 12 age-matched healthy control subjects using positron emission tomography. Symptoms were assessed using the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale. [(11)C]Ro15-4513 binding was quantified by binding potential (BP) obtained by the reference tissue model. [(11)C]Ro15-4513 binding in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus was negatively correlated with negative symptom scores in patients with schizophrenia, although there was no significant difference in BP between patients and controls. GABA(A)/BZ receptor including alpha5 subunit in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus might be involved in the pathophysiology of negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
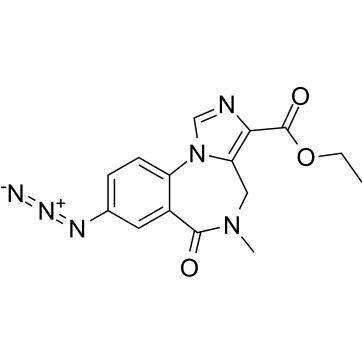 |
Ro 15-4513
CAS:91917-65-6 |
C15H14N6O3 |
|
Rats with different thresholds for DMCM-induced clonic convu...
2012-02-01 [Epilepsy Res. 98(2-3) , 216-22, (2012)] |
|
Antagonism of the ethanol-like discriminative stimulus effec...
2009-10-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 331(1) , 142-52, (2009)] |
|
Modulation of diazepam-insensitive GABA(A) receptors by micr...
2013-01-15 [Brain Res. 1490 , 1-8, (2013)] |
|
Alpha2-containing GABA(A) receptors are involved in mediatin...
2008-07-01 [Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 90(1) , 9-18, (2008)] |
|
Low concentrations of ethanol do not affect radioligand bind...
2007-08-24 [Brain Res. 1165 , 15-20, (2007)] |