Suberoyl bis-hydroxamic acid induces p53-dependent apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
Zhi-gang Zhuang, Fei Fei, Ying Chen, Wei Jin
Index: Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 29 , 1459-66, (2008)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
To study the effects of suberoyl bis-hydroxamic acid (SBHA), an inhibitor of histone deacetylases, on the apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells.Apoptosis in MCF-7 cells induced by SBHA was demonstrated by flow cytometric analysis, morphological observation, and DNA ladder. Mitochondrial membrane potential (DeltaPsim) was measured using the fluorescent probe JC-1. The expressions of p53, p21, Bax, and PUMA were determined using RT-PCR or Western blotting analysis after the MCF-7 cells were treated with SBHA or p53 siRNA.SBHA induced apoptosis in MCF-7 cells. The expressions of p53, p21, Bax, and PUMA were induced, and DeltaPsim collapsed after treatment with SBHA. p53 siRNA abrogated the SBHA-induced apoptosis and the expressions of p53, p21, Bax, and PUMA.The activation of the p53 pathway is involved in SBHA-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 cells.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
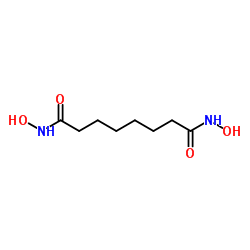 |
N,N'-Dihydroxyoctanediamide
CAS:38937-66-5 |
C8H16N2O4 |
|
A regimen combining the Wee1 inhibitor AZD1775 with HDAC inh...
2015-04-01 [Leukemia 29(4) , 807-18, (2015)] |
|
Reactive oxygen species, glutathione, and thioredoxin influe...
2015-05-01 [Tumour Biol. 36 , 3429-39, (2015)] |
|
Down-Regulation of Thioredoxin1 Is Involved in Death of Calu...
2016-05-01 [J. Cell. Biochem. 117 , 1250-61, (2016)] |
|
A Bim-targeting strategy overcomes adaptive bortezomib resis...
2014-10-23 [Blood 124(17) , 2687-97, (2014)] |
|
Evaluation of histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) as ther...
2015-08-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 23 , 5151-5, (2015)] |