In vivo metabolism of 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine (2C-B) in the rat: identification of urinary metabolites.
Tatsuyuki Kanamori, Hiroyuki Inoue, Yuko Iwata, Yoshihito Ohmae, Tohru Kishi
Index: J. Anal. Toxicol. 26(2) , 61-6, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The in vivo metabolism of 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine (2C-B), a ring-substituted psychoactive phenethylamine, in the rat was studied. Male Wistar rats were administered 10 mg/kg of 2C-B hydrochloride orally, and 24 h urine fractions were collected. After enzymatic hydrolysis of the urine samples, the metabolites were extracted by liquid-liquid extraction and analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. 2-(4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-ethanol, 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenylacetic acid, 2-(2-hydroxy-4-bromo-5-methoxyphenyl)-ethylamine, 2-(2-methoxy-4-bromo-5-hydroxyphenyl)-ethylamine, 1-acetoamino-2-(2-hydroxy-4-bromo-5-methoxyphenyl)-ethane, and 1-acetoamino-2-(2-methoxy-4-bromo-5-hydroxyphenyl)-ethane were identified as 2C-B metabolites. These findings suggest that at least two metabolic pathways for 2C-B are operative in rats. The first pathway leads to the corresponding aldehyde metabolite by deamination, which is subsequently reduced or oxidized, to give the corresponding alcohol and carboxylic acid metabolites. The second pathway leads to the corresponding 2-O-desmethyl or 5-O-desmethyl metabolites in which the amino group is subsequently acetylated.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
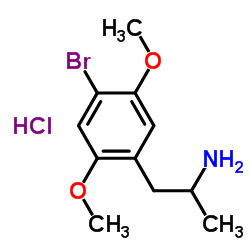 |
UNII:OII49KV8F3
CAS:29705-96-2 |
C11H17BrClNO2 |
|
Protracted effects of chronic stress on serotonin-dependent ...
2015-01-01 [Stress 18 , 668-76, (2015)] |
|
Beta-oxygenated analogues of the 5-HT2A serotonin receptor a...
2004-11-18 [J. Med. Chem. 47(24) , 6034-41, (2004)] |
|
A study of the metabolism of methamphetamine and 4-bromo-2,5...
2005-03-10 [Forensic Sci. Int. 148(2-3) , 131-7, (2005)] |
|
2,5-Dimethoxyamphetamine-derived designer drugs: studies on ...
2008-12-15 [Toxicol. Lett. 183(1-3) , 52-7, (2008)] |
|
'Hybrid' benzofuran-benzopyran congeners as rigid analogs of...
2008-06-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16(11) , 6242-51, (2008)] |