Type I Interferons Control Proliferation and Function of the Intestinal Epithelium.
Yuliya V Katlinskaya, Kanstantsin V Katlinski, Audrey Lasri, Ning Li, Daniel P Beiting, Amy C Durham, Ting Yang, Eli Pikarsky, Christopher J Lengner, F Brad Johnson, Yinon Ben-Neriah, Serge Y Fuchs
Index: Mol. Cell. Biol. 36 , 1124-35, (2016)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Wnt pathway-driven proliferation and renewal of the intestinal epithelium must be tightly controlled to prevent development of cancer and barrier dysfunction. Although type I interferons (IFN) produced in the gut under the influence of microbiota are known for their antiproliferative effects, the role of these cytokines in regulating intestinal epithelial cell renewal is largely unknown. Here we report a novel role for IFN in the context of intestinal knockout of casein kinase 1α (CK1α), which controls the ubiquitination and degradation of both β-catenin and the IFNAR1 chain of the IFN receptor. Ablation of CK1α leads to the activation of both β-catenin and IFN pathways and prevents the unlimited proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells despite constitutive β-catenin activity. IFN signaling contributes to the activation of the p53 pathway and the appearance of apoptotic and senescence markers in the CK1α-deficient gut. Concurrent genetic ablation of CK1α and IFNAR1 leads to intestinal hyperplasia, robust attenuation of apoptosis, and rapid and lethal loss of barrier function. These data indicate that IFN play an important role in controlling the proliferation and function of the intestinal epithelium in the context of β-catenin activation. Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
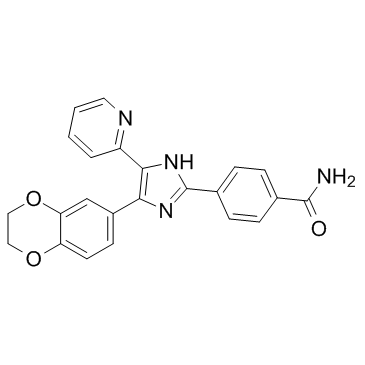 |
D4476
CAS:301836-43-1 |
C23H18N4O3 |
|
Acetylation of Beclin 1 inhibits autophagosome maturation an...
2015-01-01 [Nat. Commun. 6 , 7215, (2015)] |
|
Small molecule-directed immunotherapy against recurrent infe...
2014-06-06 [J. Biol. Chem. 289(23) , 16508-16515, (2014)] |
|
The selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors: a further upda...
2007-12-15 [Biochem. J. 408 , 297-315, (2007)] |
|
D4476, a cell-permeant inhibitor of CK1, suppresses the site...
2004-01-01 [EMBO J. Rep. 5 , 60-65, (2004)] |