Analgesic synergy between topical morphine and butamben in mice.
Yuri A Kolesnikov, Marcela Cristea, Gavril W Pasternak
Index: Anesth. Analg. 97(4) , 1103-7, table of contents, (2003)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Studies have revealed that lidocaine is an effective analgesic when applied topically to the tail of a mouse in the radiant heat tail-flick assay. In addition, the topical combination of lidocaine with morphine revealed synergistic interactions between the two drugs. In the current studies, we demonstrate that topical butamben, benzocaine, and bupivacaine are active in the radiant heat tail-flick assay. In this assay, topical lidocaine has a ceiling effect and displays a biphasic curve, with large doses markedly decreasing the responses almost to baseline levels. In contrast, butamben has an S-shape dose-dependent response in the assay and did not display a biphasic curve as seen with lidocaine, suggesting that topical butamben may have advantages over lidocaine. Both benzocaine and bupivacaine also showed dose-dependent analgesic activity in this model. Like lidocaine, butamben/morphine combinations displayed synergistic interactions. Indeed, the synergy appeared more prominent with a butamben/morphine combination. We also observed synergy between topical benzocaine and morphine. Although the bupivacaine/morphine combination was suggestive of synergy on isobolographic analysis, it did not achieve statistical significance. These studies indicate that a series of local anesthetics are all active topically in the radiant heat tail-flick assay in mice and that several interact synergistically with morphine. Of the local anesthetics tested, butamben seemed to have several pharmacological characteristics, alone and in combination with morphine, which suggest that it may be superior to the other local anesthetics. Together, these observations suggest that topical combinations of opioids and local anesthetics may prove clinically valuable.Topical administration of the opioid micro -agonist morphine and the sodium channel inhibitors butamben and benzocaine results in a synergistic interaction for antinociception in radiant heat tail-flick assay in mice, suggesting that the combination of these drugs will enhance rather than detract from the analgesia of either alone.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
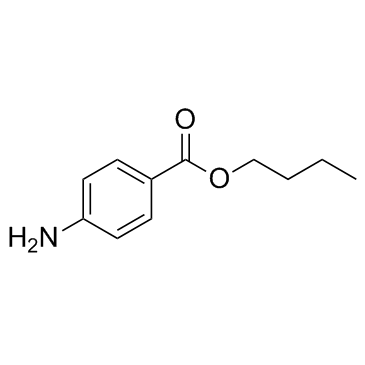 |
butamben
CAS:94-25-7 |
C11H15NO2 |
|
Inhibition of sensory neuronal TRPs contributes to anti-noci...
2012-01-11 [Neurosci. Lett. 506(2) , 297-302, (2012)] |
|
Butamben derivatives enhance BMP-2-stimulated commitment of ...
2011-12-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 21 , 7363-6, (2011)] |
|
Benzoate X receptors alpha and beta are pharmacologically di...
2002-11-15 [J. Biol. Chem. 277(46) , 43691-7, (2002)] |
|
Nerve blocks with 5% butamben suspension for the treatment o...
1998-01-01 [Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 23(4) , 395-401, (1998)] |
|
Identification of a yellow impurity in aged samples of aqueo...
2000-06-01 [J. Pharm. Sci. 89(6) , 766-70, (2000)] |