Mutagenicity of N-OH-MOCA (4-amino-4'-hydroxylamino-bis-3,3'-dichlorodiphenylmethane) and PBQ (2-phenyl-1,4-benzoquinone) in human lymphoblastoid cells.
T M Reid, D G DeBord, K L Cheever, R E Savage
Index: Toxicol. Lett. 95(3) , 205-10, (1998)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The genotoxic potential of two occupationally significant chemicals, 4,4'-methylene-bis-2-chloroaniline (MOCA) and 2-phenyl-1,4-benzoquinone (PBQ), was explored by monitoring the induction of mutations at the HPRT locus of AHH-1 human lymphoblastoid cells. Exposure of AHH-1 cells to the putative carcinogenic metabolite of MOCA, N-OH-MOCA, induced a 6-fold increase in mutant frequency and resulted in base pair substitutions primarily at A:T base pairs. In contrast, exposure to PBQ did not result in an increased mutant frequency although this compound was significantly more cytotoxic than N-OH-MOCA at equimolar doses. The induction of mutations at A:T sites by N-OH-MOCA is consistent with the type of DNA damage known to be produced by MOCA and provides a specific marker of genotoxic damage for exposed populations.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
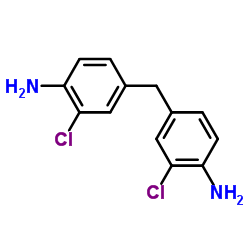 |
4,4'-methylene-bis-(2-chloroaniline)
CAS:101-14-4 |
C13H12Cl2N2 |
|
[Resolution of overlapping mass spectra of azobiphenyl dyes ...
2001-03-01 [Se Pu 19(2) , 184-7, (2001)] |
|
New approaches to extraction techniques in determination of ...
2012-05-15 [Talanta 93 , 117-21, (2012)] |
|
Oxidative DNA damage estimated by plasma 8-hydroxydeoxyguano...
2007-09-01 [J. Occup. Health 49(5) , 389-98, (2007)] |
|
A survey of occupational exposure to 4,4'-methylene-bis (2-c...
2009-07-01 [Ann. Occup. Hyg. 53(5) , 499-507, (2009)] |
|
Bladder cancer screening and monitoring of 4,4'-methylenebis...
2005-08-01 [Urology 66(2) , 305-10, (2005)] |