Growth of Staphylococcus epidermidis in anaesthetic resuscitative drugs: implications for potential contamination.
C Wu, C Engler, R Norton
Index: Anaesth. Intensive Care 33(1) , 69-72, (2005)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
This controlled laboratory study investigated the survival of Staphylococcus epidermidis (S. epidermidis) over a 24 hour period in four commonly drawn-up anaesthetic resuscitative drugs: suxamethonium, atropine, metaraminol and ephedrine. These drugs were prepared in typical therapeutic concentrations and then inoculated with S. epidermidis. Samples of the inoculated drug preparations were cultured on horse blood agar plates at 0, 2, 6, 12 and 24 hourly intervals and incubated for 24 hours. Colony counts were performed at the end of the incubation period. Suxamethonium, atropine and metaraminol all showed an inhibitory effect on colony counts within the first six hours. There was a more gradual decline of colony counts over a 24 hour period in the ephedrine solution. This decline was similar to that occurring in the normal saline. It is concluded that suxamethonium, atropine and metaraminol do not support the survival of the common skin contaminant, S. epidermidis over a 24 hour period.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
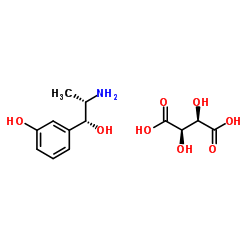 |
Metaraminol bitartrate
CAS:33402-03-8 |
C13H19NO8 |
|
Pharmacokinetic study of three cardiovascular drugs by high-...
2007-10-15 [J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 858(1-2) , 42-8, (2007)] |
|
Norepinephrine and metaraminol in septic shock: a comparison...
2005-05-01 [Intensive Care Med. 31(5) , 634-7, (2005)] |
|
The blood-brain barrier for catecholamines - revisited.
2007-04-01 [Neurotox. Res. 11(3-4) , 261-71, (2007)] |
|
Metaraminol (Aramine) in the management of a significant aml...
2005-07-01 [Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 24(7) , 377-81, (2005)] |
|
Effect of dopamine and metaraminol on the renal function of ...
2007-04-20 [Chin. Med. J. 120(8) , 680-3, (2007)] |