Properties controlling the diffusion and release of water-soluble solutes from poly(ethylene oxide) hydrogels. 4. Extended constant rate release from partly-coated spheres.
M E McNeill, N B Graham
Index: J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 7(11) , 953-63, (1996)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Spheres of poly(ethylene oxide) xerogel from 4-17 mm diameter were impregnated with the drug, proxyphylline, or the herbicide, 2,4-DNa and then partly coated with a water-impermeable elastomer. When placed in water the active additive was released over periods ranging from hours to weeks at a nearly constant rate. The effect of the hydrogel sphere dimensions and the window size through the elastomer, on water uptake and consequent release of the active agent were examined. These devices superficially possess a configuration similar to some commercial osmotic devices though the active-agent release from the devices of this paper is, in fact, diffusive and not osmotically driven. They appear to provide a very versatile and simple design allowing relatively constant release of the active agent over periods of hours to months merely by changing the device geometry.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
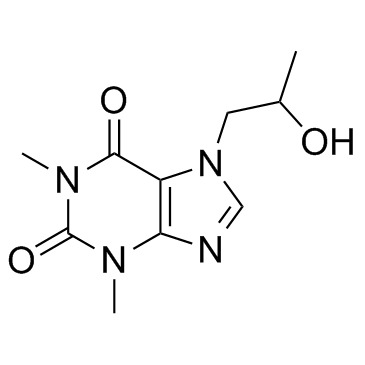 |
Proxyphylline
CAS:603-00-9 |
C10H14N4O3 |
|
Endocrine regulation of airway contractility is overlooked.
2014-08-01 [J. Endocrinol. 222(2) , R61-73, (2014)] |
|
High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of (R)...
[J. Chromatogr. A. 491(2) , 355-66, (1989)] |
|
Acute intoxication with theophylline, proxyphylline and dipr...
1990-01-01 [Acta Paediatr. Scand. 79(1) , 112-4, (1990)] |
|
Rheology of polyol behenates and drug release from matrix mo...
1999-05-25 [Int. J. Pharm. 182(2) , 145-54, (1999)] |
|
Properties controlling the diffusion and release of water-so...
1993-01-01 [J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 5(1-2) , 111-30, (1993)] |