Development of a new quantitative method for detection of endotoxin by fluorescence labeling of 3-hydroxy fatty acid.
K Tanamoto
Index: Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 256 , 203-213, (1990)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
New quantitative method for the detection of minute amounts of endotoxin has been developed using 3-hydroxytetradecanoic acid as a chemical marker. After converting 3-hydroxytetradecanoic acid to methyl ester, it was coupled with a fluorescent probe, anthracene-9-carboxyl chloride, obtained by chlorization of 9-anthroic acid with oxalyl chloride. The resulting ester was isolated by HPLC on silica column. The purified product, methyl-3-0-(9-carboxy-anthracenyl) tetradecanoate (M/Z 462), was highly responsive to a fluorescence spectrophotometer, showing maximum emission with excitation wavelength at 257 nm and emission wavelength at 458 nm in dichloromethane, the limit of detection being as little as 10 f mol. Using this method it is currently possible to detect Salmonella abortus equi endotoxin in aqueous solution at a level of 100 pg.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
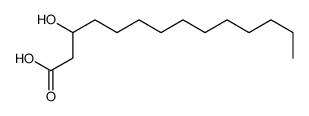 |
DL-B-HYDROXYMYRISTIC ACID
CAS:3422-31-9 |
C14H28O3 |
|
Direct enantioseparation of underivatized aliphatic 3-hydrox...
2014-10-10 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1363 , 101-8, (2014)] |
|
Determination of monomeric composition in polyhydroxyalkanoa...
2016-01-01 [Talanta 146 , 107-13, (2015)] |
|
The evaluation of the role of beta-hydroxy fatty acids on ch...
2006-01-01 [Mediators Inflamm. 2006 , 64980, (2006)] |
|
Long-chain 3-hydroxy fatty acids accumulating in LCHAD and M...
2010-07-01 [Neurochem. Int. 56 , 930-936, (2010)] |
|
Production and characterization of medium-chain-length polyh...
2007-10-01 [Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 76 , 1153-1159, (2007)] |