Inhibition of excitatory amino acid-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat hippocampus by L-aspartate-beta-hydroxamate.
G C Ormandy
Index: Brain Res. 572(1-2) , 103-7, (1992)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The effect of a series of glutamate uptake inhibitors was tested on ibotenate-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis. The pharmacological profile of the inhibitory effect of these compounds on the ibotenate response was quite different from that on glutamate uptake. Aspartate-beta-hydroxamate was the most potent compound with the L-isomer (IC50 11 +/- 2 microM) being considerably more potent than the D-isomer (IC50 104 +/- 12 microM). The effect of the L-aspartate-beta-hydroxamate was found to be specific for ibotenate and quisqualate-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis; this compound did not affect hydrolysis stimulated by carbachol, K+ or sodium fluoride. The inhibition of the ibotenate response was found to involve a non-competitive and irreversible mechanism.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
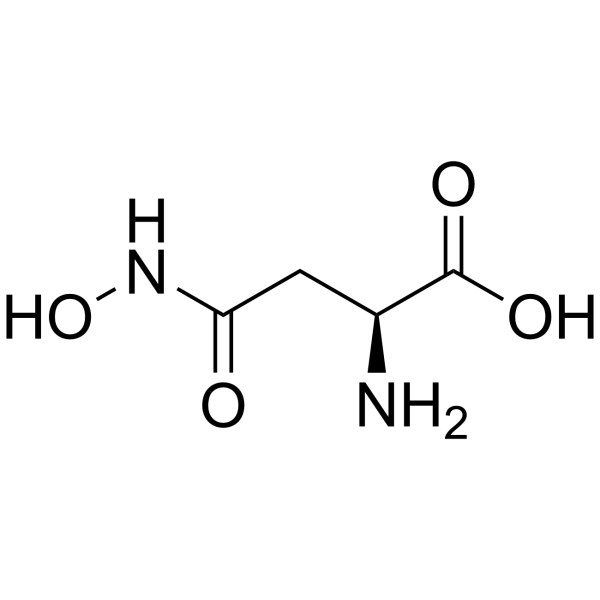 |
L-Asparagine,N-hydroxy
CAS:1955-68-6 |
C4H8N2O4 |
|
Blockade of PD1 and TIM3 restores innate and adaptive immuni...
2015-03-01 [Gastroenterology 148(3) , 590-602.e10, (2015)] |
|
Continuous and pulsed hydrogen-deuterium exchange and mass s...
2015-10-27 [Biochemistry 54 , 6475-81, (2015)] |
|
A Novel Role of E-Cadherin-Based Adherens Junctions in Neopl...
2015-01-01 [PLoS ONE 10 , e0133578, (2015)] |
|
Hydroxamic acids as a novel family of serine racemase inhibi...
2009-10-08 [J. Med. Chem. 52 , 6032-41, (2009)] |
|
Estrogen-dependent regulation of human uterine natural kille...
2015-06-01 [Hum. Reprod. 30 , 1290-301, (2015)] |