Synthesis and characterization of poly(dimer acid-brassylic acid) copolymer and poly(dimer acid-pentadecandioic acid) copolymer.
Wen-xun Guo, Kai-xun Huang
Index: Biopolymers 74(3) , 248-55, (2004)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Poly(dimer acid-brassylic acid) [P(DA-BA)] copolymers and poly(dimer acid-pentadecandioic acid) [P(DA-PA)] copolymers were prepared by melt polycondensation of the corresponding mixed anhydride prepolymers. The copolymers were characterized by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), gel permeation chromatography (GPC), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), wide angle x-ray powder-diffraction, and thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA). In vitro studies show that all the copolymers are degradable in phosphate buffer at 37 degrees C, and leaving an oily dimer acid residue after hydrolysis for the copolymer with high content of dimer acid. The release profiles of hydrophilic model drug, ciprofloxcin hydrochloride, from the copolymers, follow first-order release kinetics. All the preliminary results suggested that the copolymer might be potentially used as drug delivery devices.Copyright 2004 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Biopolymers, 2004
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
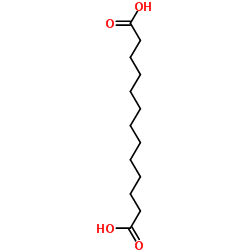 |
Tridecanedioic acid
CAS:505-52-2 |
C13H24O4 |
|
Pseudohomogeneous kinetic study on a two-liquid-phase fermen...
1994-01-01 [Chin. J. Biotechnol. 10(4) , 271-82, (1994)] |
|
[Search for yeast producers of brassylic and sebacic fatty a...
2004-01-01 [Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol. 40(5) , 533-5, (2004)] |
|
[Studies on microbial production of undecane 1, 11-dicarboxy...
1999-06-01 [Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 39(3) , 279-81, (1999)] |
|
Macrocyclic musk compounds--an absence of genotoxicity in th...
2002-09-05 [Toxicol. Lett. 135(1-2) , 155-63, (2002)] |
|
Mass spectrometric identification of 2-hydroxy-sebacic acid ...
1986-06-01 [Biomed. Environ. Mass Spectrom. 13(6) , 315-8, (1986)] |