Photoconsumption of molecular oxygen on both donor and acceptor sides of photosystem II in Mn-depleted subchloroplast membrane fragments.
Denis V Yanykin, Andrei A Khorobrykh, Sergey A Khorobrykh, Vyacheslav V Klimov
Index: Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1797(4) , 516-23, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Oxygen consumption in Mn-depleted photosystem II (PSII) preparations under continuous and pulsed illumination is investigated. It is shown that removal of manganese from the water-oxidizing complex (WOC) by high pH treatment leads to a 6-fold increase in the rate of O(2) photoconsumption. The use of exogenous electron acceptors and donors to PSII shows that in Mn-depleted PSII preparations along with the well-known effect of O(2) photoreduction on the acceptor side of PSII, there is light-induced O(2) consumption on the donor side of PSII (nearly 30% and 70%, respectively). It is suggested that the light-induced O(2) uptake on the donor side of PSII is related to interaction of O(2) with radicals produced by photooxidation of organic molecules. The study of flash-induced O(2) uptake finds that removal of Mn from the WOC leads to O(2) photoconsumption with maximum in the first flash, and its yield is comparable with the yield of O(2) evolution on the third flash measured in the PSII samples before Mn removal. The flash-induced O(2) uptake is drastically (by a factor of 1.8) activated by catalytic concentration (5-10microM, corresponding to 2-4 Mn per RC) of Mn(2+), while at higher concentrations (>100microM) Mn(2+) inhibits the O(2) photoconsumption (like other electron donors: ferrocyanide and diphenylcarbazide). Inhibitory pre-illumination of the Mn-depleted PSII preparations (resulting in the loss of electron donation from Mn(2+)) leads to both suppression of flash-induced O(2) uptake and disappearance of the Mn-induced activation of the O(2) photoconsumption. We assume that the light-induced O(2) uptake in Mn-depleted PSII preparations may reflect not only the negative processes leading to photoinhibition but also possible participation of O(2) or its reactive forms in the formation of the inorganic core of the WOC.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
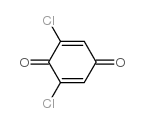 |
2,6-DICHLORO-1,4-BENZOQUINONE
CAS:697-91-6 |
C6H2Cl2O2 |
|
Metal-independent decomposition of hydroperoxides by halogen...
2009-07-14 [Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106(28) , 11466-71, (2009)] |
|
Removal of halo-benzoquinone (emerging disinfection by-produ...
2013-04-01 [Water Res. 47(5) , 1773-82, (2013)] |
|
Microbial anaerobic demethylation and dechlorination of chlo...
2004-01-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70(1) , 385-92, (2004)] |
|
Interaction of exogenous quinones with membranes of higher p...
2003-06-05 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1604(2) , 115-23, (2003)] |
|
Substrate water exchange in photosystem II core complexes of...
2014-08-01 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1837(8) , 1257-62, (2014)] |