Development and characterization of rhVEGF-loaded poly(HEMA-MOEP) coatings electrosynthesized on titanium to enhance bone mineralization and angiogenesis.
Elvira De Giglio, Stefania Cometa, Maria Antonietta Ricci, Antonio Zizzi, Damiana Cafagna, Sandra Manzotti, Luigia Sabbatini, Monica Mattioli-Belmonte
Index: Acta Biomater. 6(1) , 282-90, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Osteointegration of titanium implants could be significantly improved by coatings capable of promoting both mineralization and angiogenesis. In the present study, a copolymeric hydrogel coating, poly-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphate (P(HEMA-MOEP)), devised to enhance calcification in body fluids and to entrap and release growth factors, was electrosynthesized for the first time on titanium substrates and compared to poly-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (PHEMA), used as a blank reference. Polymers exhibiting negatively charged groups, such as P(HEMA-MOEP), help to enhance implant calcification. The electrosynthesized coatings were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy. MG-63 human osteoblast-like cell behaviour on the coated specimens was investigated by scanning electron microscopy, MTT viability test and osteocalcin mRNA detection. The ability of negatively charged phosphate groups to promote hydroxyapatite-like calcium phosphate deposition on the implants was explored by immersing them in simulated body fluid. Similar biological responses were observed in both coated specimens, while calcium-phosphorus globules were detected only on P(HEMA-MOEP) surfaces pretreated with alkaline solution. Testing of the ability of P(HEMA-MOEP) hydrogels to entrap and release human recombinant vascular endothelial growth factor, to tackle the problem of insufficient oxygen and nutrient delivery, suggested that P(HEMA-MOEP)-coated titanium prostheses could represent a multifunctional material suitable for bone restoration applications.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
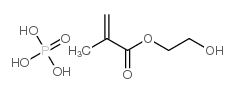 |
2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate acid phosphate
CAS:52628-03-2 |
C6H13O7P |
|
Deposition of a hydroxyapatite thin layer onto a polymer sur...
1996-12-01 [J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 32(4) , 687-91, (1996)] |
|
Investigation into the diffusion of water into HEMA-co-MOEP ...
2004-01-01 [Biomacromolecules 5(4) , 1194-9, (2004)] |
|
In vitro bioactivity of MOEP grafted ePTFE membranes for cra...
2005-09-01 [Biomaterials 26(26) , 5303-12, (2005)] |
|
Influence of a diene impurity on the molecular structure of ...
2008-07-28 [Chem. Commun. (Camb.) (28) , 3314-6, (2008)] |
|
An advance in condensable composites.
[Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. Suppl. (23) , S3-5, (1999)] |