Identification of 3-hydroxypalmitic acid methyl ester as a novel autoregulator controlling virulence in Ralstonia solanacearum.
A B Flavier, S J Clough, M A Schell, T P Denny
Index: Mol. Microbiol. 26(2) , 251-9, (1997)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Expression of virulence genes in Ralstonia solanacearum, a phytopathogenic bacterium, is controlled by a complex regulatory network that integrates multiple signal inputs. Production of several virulence determinants is coordinately reduced by inactivation of phcB, but is restored by growth in the presence of a volatile extracellular factor (VEF) produced by wild-type strains of R. solanacearum. The VEF was purified from spent culture broth by distillation, solvent extraction, and liquid chromatography. Gas chromatography and mass spectroscopy identified 3-hydroxypalmitic acid methyl ester (3-OH PAME) as the major component in the single peak of VEF activity. Authentic 3-OH PAME and the purified VEF were active at < or =1 nM, and had nearly equivalent specific activities for stimulating the expression of eps (the biosynthetic locus for extracellular polysaccharide) in a phcB mutant. Authentic 3-OH PAME also increased the production of three virulence factors by a phcB mutant over 20-fold to wild-type levels, restored normal cell density-associated expression of eps and increased expression of eps when delivered via the vapour phase. Reanalysis of the PhcB amino acid sequence suggested that it is a small-molecule S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase, which might catalyse synthesis of 3-OH PAME from a naturally occurring fatty acid. Biologically active concentrations of extracellular 3-OH PAME were detected before the onset of eps expression, suggesting that it is an intercellular signal that autoregulates virulence gene expression in wild-type R. solanacearum. Other than acyl-homoserine lactones, 3-OH PAME is the only endogenous fatty acid derivative shown to be an autoregulator and may be the first example of a new family of compounds that can mediate long-distance intercellular communication.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
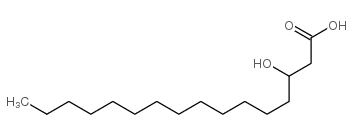 |
3-Hydroxyhexadecanoic Acid
CAS:928-17-6 |
C16H32O3 |
|
Determination of monomeric composition in polyhydroxyalkanoa...
2016-01-01 [Talanta 146 , 107-13, (2015)] |
|
Characterization of bacteria degrading 3-hydroxy palmitic ac...
2015-05-01 [Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 60(5) , 447-55, (2015)] |
|
Mitochondrial bioenergetics deregulation caused by long-chai...
2014-09-01 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1842(9) , 1658-67, (2014)] |
|
Long-chain 3-hydroxy fatty acids accumulating in LCHAD and M...
2010-07-01 [Neurochem. Int. 56 , 930-936, (2010)] |
|
Burkholderia mallei expresses a unique lipopolysaccharide mi...
2007-01-01 [Mol. Microbiol. 63 , 379-390, (2007)] |