Synthesis, structure, redox properties and azide binding for a series of biphenyl-based Cu(II) complexes.
Jacky Chen, Robert Russo, Wilson Chao, Lawrence D Margerum, Mitchell R Malachowski, Ryan White, Zachary Thawley, Angelina Thayer, Arnold L Rheingold, Lev N Zakharov
Index: Dalton Trans. (24) , 2571-9, (2007)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A series of biphenyl-based N(3)O ligands, 2, 4, 6, and 8 were synthesized and their Cu(II) complexes prepared. These complexes were characterized by a combination of elemental analysis, FAB-MS, UV-vis spectroscopy and electrochemistry. The structure of [Cu(N(3)O-mpy-NO2)Cl2], 12 [N(3)O-mpy = 2-(3-pyridylmethylimino)-2'-(2-methylaminophenol)biphenyl], was solved and showed that the ligand coordinates through the three nitrogens with the phenol oxygen uncoordinated. Titration of azide anion into solutions of the complexes in methanol resulted in the appearance of a new band between 485-495 nm at the expense of the starting peak at 380 nm. Cyclic voltammetry studies indicated that the complexes undergo quasi-reversible one-electron reductions in acetonitrile at potentials between 0.13-0.58 V vs. Ag/AgCl. The complexes were found to be weakly active for the oxidation of di-tert-butyl catechol (DTBC).
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
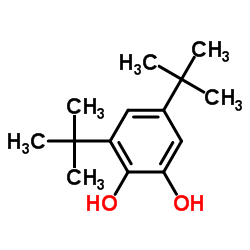 |
3,5-Di-t-butylcatechol
CAS:1020-31-1 |
C14H22O2 |
|
Catechol oxidase activity of a series of new dinuclear coppe...
2008-08-18 [Inorg. Chem. 47(16) , 7083-93, (2008)] |
|
3,5-Di-t-butyl catechol is a potent human ryanodine receptor...
2012-07-01 [Pharmacol. Res. 66(1) , 80-7, (2012)] |
|
A novel tripodal ligand containing three different N-heteroc...
2009-01-01 [Chemistry 15(22) , 5567-76, (2009)] |
|
Chemistry of singlet oxygen--48. Isolation and structure of ...
1987-09-01 [Photochem. Photobiol. 46(3) , 325-30, (1987)] |
|
3,5-di-t-butylcatechol (DTCAT) as an activator of rat skelet...
2005-02-01 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 69(3) , 485-91, (2005)] |