Desorption chemical ionization and fast atom bombardment mass spectrometric studies of the glucuronide metabolites of doxylamine.
J O Lay, W A Korfmacher, D W Miller, P Siitonen, C L Holder, A B Gosnell
Index: Biomed. Environ. Mass Spectrom. 13(11) , 627-32, (1986)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Three glucuronide metabolites of doxylamine succinate were collected in a single fraction using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) from the urine of dosed male Fischer 344 rats. The metabolites were then separated using an additional HPLC step into fractions containing predominantly a single glucuronide metabolite. Analysis of the metabolites by methane and ammonia desorption chemical ionization, with and without derivatization, revealed fragment ions suggestive of a hydroxylated doxylamine moiety. Identification of the metabolites as glucuronides of doxylamine, desmethyldoxylamine and didesmethyldoxylamine was accomplished, based on determination of the molecular weight and exact mass of each metabolite using fast atom bombardment (FAB) ionization. This assignment was confirmed by the fragmentation observed in FAB mass spectrometric and tandem mass spectrometric experiments. Para-substitution of the glucuronide on the phenyl moiety was observed by 500-MHz nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrometry. A fraction containing all three glucuronide metabolites, after a single stage of HPLC separation, was also analysed by FAB mass spectrometry, and the proton- and potassium-containing quasimolecular ions for all three metabolites were observed.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
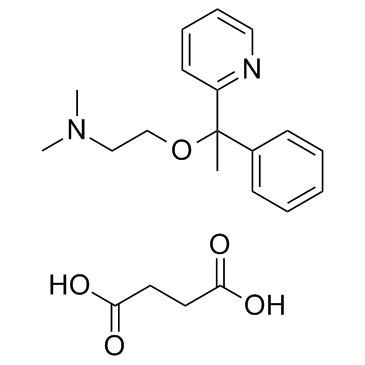 |
DOXYLAMINE SUCCINATE
CAS:562-10-7 |
C21H28N2O5 |
|
Use of In Vitro Morphogenesis of Mouse Embryoid Bodies to As...
2016-01-01 [Toxicol. Sci. 149 , 15-30, (2016)] |
|
[Nontraumatic rhabdomyolysis due to oral poisoning by doxyla...
1997-03-08 [Med. Clin. (Barc.) 108(9) , 356, (1997)] |
|
Safety assessment of OTC drugs: doxylamine succinate.
1995-01-01 [Arch. Toxicol. Suppl. 17 , 326-40, (1995)] |
|
Dose-response trend tests for tumorigenesis, adjusted for bo...
1999-06-01 [Toxicol. Sci. 49(2) , 318-23, (1999)] |
|
Metabolism of doxylamine succinate in Fischer 344 rats. Part...
1987-01-01 [J. Anal. Toxicol. 11(3) , 113-21, (1987)] |