Vitamin C-sulfate inhibits mineralization in chondrocyte cultures: a caveat.
A L Boskey, R D Blank, S B Doty, Adele L. Boskey, Robert D. Blank, Stephen B. Doty
Index: Matrix Biol. 20(2) , 99-106, (2001)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Differentiating chick limb-bud mesenchymal cell micro-mass cultures routinely mineralize in the presence of 10% fetal calf serum, antibiotics, 4 mM inorganic phosphate (or 2.5 mM beta-glycerophosphate), 0.3 mg/ml glutamine and either 25 microg/ml vitamin C or 5-12 microg/ml vitamin C-sulfate. The failure of these cultures to produce a mineralized matrix (assessed by electron microscopy, 45Ca uptake and Fourier transform infrared microscopy) led to the evaluation of each of these additives. We report here that the "stable" vitamin C-sulfate (ascorbic acid-2-sulfate) causes increased sulfate incorporation into the cartilage matrix. Furthermore, the release of sulfate from the vitamin C derivative appears to be responsible for the inhibition of mineral deposition, as demonstrated in cultures with equimolar amounts of vitamin C and sodium sulfate.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
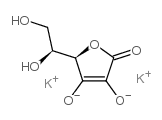 |
L-Ascorbic acid 2-sulfate dipotassium salt
CAS:52174-99-9 |
C6H6K2O6 |
|
Identification of sulfation sites of metabolites and predict...
2006-10-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 386(3) , 666-74, (2006)] |
|
L-ascorbyl-2-sulfate alleviates Atlantic salmon scurvy.
1994-09-01 [Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 206(4) , 421-4, (1994)] |
|
Quantitative analysis of ascorbic acid-2-sulfate by high-per...
[J. Chromatogr. A. 308 , 306-9, (1984)] |
|
Specific determination of arylsulfatase A activity.
1986-01-15 [Experientia 42(1) , 33-5, (1986)] |
|
Isolation and characterization of rat hepatic ascorbic acid-...
1987-01-01 [Enzyme 37(3) , 134-40, (1987)] |