Rapid free chlorine decay in the presence of Cu(OH)2: chemistry and practical implications.
Caroline K Nguyen, Kim A Powers, Meredith A Raetz, Jeffrey L Parks, Marc A Edwards
Index: Water Res. 45(16) , 5302-12, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A rapid reaction between free chlorine and the cupric hydroxide [Cu(OH)2] solids commonly found on pipe walls in premise plumbing can convert free chlorine to chloride and rapidly age Cu(OH)2 to tenorite (CuO). This reaction has important practical implications for maintaining free chlorine residuals in premise plumbing, commissioning of new copper pipe systems, and maintaining low levels of copper in potable water. The reaction stoichiometry between chlorine and Cu(OH)2 is consistent with formation of CuO through a metastable Cu(III) intermediate, although definitive mechanistic understanding requires future research. Natural levels of silica in water (0-30 mg/L), orthophosphate, and higher pH interfere with the rate of this reaction.Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
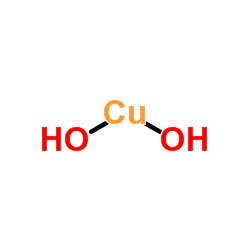 |
Cupric hydroxide
CAS:20427-59-2 |
Cu.(OH)2 |
|
Synthesis of hierarchical three-dimensional copper oxide nan...
2013-09-07 [Nanoscale 5(17) , 7991-7, (2013)] |
|
The Goldilocks principle in action: synthesis and structural...
2013-09-14 [Dalton Trans. 42(34) , 12265-73, (2013)] |
|
Physical and chemical control of released microorganisms at ...
1991-09-01 [Can. J. Microbiol. 37(9) , 708-12, (1991)] |
|
Continuous biotreatment of copper-concentrated solutions by ...
2006-01-01 [Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 128(1) , 23-32, (2006)] |
|
Corrosion investigation of two materials for implant supraco...
1991-04-01 [Scand. J. Dent. Res. 99(2) , 181-6, (1991)] |