| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
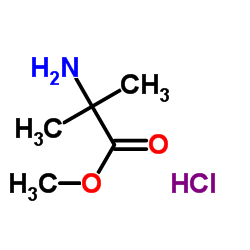 |
H-Aib-OMe.HCl
CAS:15028-41-8 |
J W Tsang, B Schmied, R Nyfeler, M Goodman
Index: J. Med. Chem. 27 , 1663-1668, (1984)
Full Text: HTML
Stereochemical and structural aspects of the variations in the C-terminal residue of L-aspartyl-L-phenylalanine methyl ester have been investigated. Novel configurational analogues such as L-aspartyl-D-alanine benzyl ester and L-aspartyl-D-alpha-aminobutyric acid benzyl ester were found to be sweet. In addition, chiral and achiral alpha, alpha-dialkylglycine and alpha-aminocycloalkanecarboxylic acids were incorporated into the dipeptides. The L-aspartic acid based dipeptide derivatives of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid methyl ester, alpha-aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid methyl ester, alpha-aminocyclobutanecarboxylic acid methyl ester, and alpha-aminocyclopentanecarboxylic acid methyl ester are sweet. Dipeptides with alpha-aminocyclohexanecarboxylic acid methyl ester and alpha-aminocycloheptanecarboxylic acid methyl ester are bitter, whereas the analogues with alpha-aminocyclooctanecarboxylic acid methyl ester, alpha, alpha-diethylglycine methyl ester, and alpha-aminoisobutyric acid benzyl ester are tasteless. Aspects on chirality and effective volume of the C-terminal residue are discussed and correlated with taste.
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
H-Aib-OMe.HCl
CAS:15028-41-8 |
C5H12ClNO2 |
|
An efficient and expedient method for the synthesis of 11C-l...
2011-04-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 21 , 2437-2440, (2011)] |
|
Characterization of glycine transport in cultured Müller gli...
1999-06-01 [Glia 26 , 273-279, (1999)] |
|
Effects of exogenous excitatory amino acid neurotransmitters...
2009-07-01 [Neurochem. Res. 34 , 1249-1254, (2009)] |
Home | MSDS/SDS Database Search | Journals | Product Classification | Biologically Active Compounds | Selling Leads | About Us | Disclaimer
Copyright © 2024 ChemSrc All Rights Reserved