On the quantification of mixing in microfluidics.
Ali Hashmi, Jie Xu
Index: J. Lab. Autom. 19(5) , 488-91, (2014)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Methods for quantifying mixing in microfluidics have varied largely in the past, and various indices have been employed to represent the extent of mixing. Mixing between two or more colored liquids is usually quantified using simple mathematical functions operated over a sequence of images. The function, usually termed mixing indices, involves a measure of standard deviation. Here, we first review some mixing indices and then experimentally verify the index most representative of a mixing event. It is observed that the relative mixing index is not affected by the lighting conditions, unlike other known mixing indices. Based on this finding, the use of a relative mixing index is advocated for further use in the lab-on-a-chip community for quantifying mixing events. © 2014 Society for Laboratory Automation and Screening.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
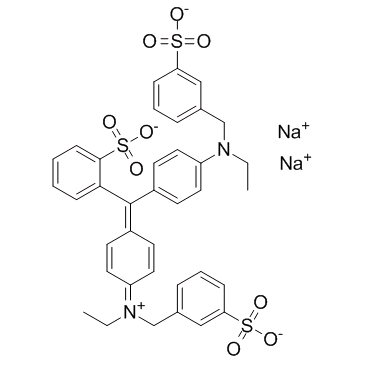 |
Brilliant Blue FCF
CAS:3844-45-9 |
C37H34N2Na2O9S3 |
|
Toxic effects of some synthetic food colorants and/or flavor...
2013-03-01 [Toxicol. Ind. Health 29(2) , 224-32, (2013)] |
|
Simultaneous cloud point extraction and spectrophotometric d...
2011-03-15 [Talanta 84(1) , 240-3, (2011)] |
|
Triacontanol hormone stimulates population, growth and Brill...
2010-10-15 [J. Hazard. Mater. 182(1-3) , 525-30, (2010)] |
|
Absorption of triphenylmethane dyes Brilliant Blue and Paten...
2013-02-01 [Food Chem. Toxicol. 52 , 19-27, (2013)] |
|
Combined effects of sugarcane bagasse extract and synthetic ...
2010-11-15 [J. Hazard. Mater. 183(1-3) , 497-505, (2010)] |